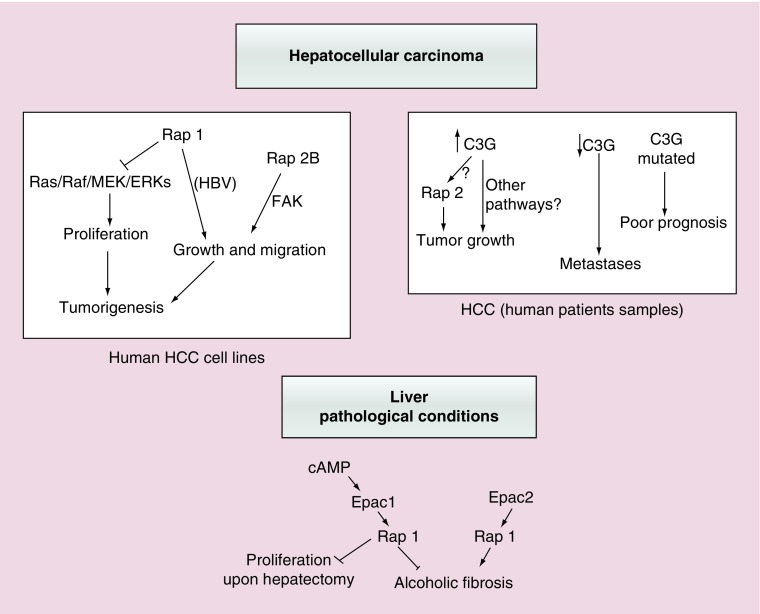
Figure 6. . Functions of Rap proteins and its GEFs in hepatocellular carcinoma or other liver pathologies.
This scheme summarizes the most relevant actions of Rap1/2 and their main GEFs, Epac and C3G, in different liver pathological contexts. Upper left panel shows both the anti- and pro-tumorigenic effect of Rap1, as well as that of Rap2B promoting tumor growth and migration in human HCC cell lines. The potential implication of Ras/ERKs cascade and FAK is also indicated. Upper right panel reflects the positive or negative correlation between C3G levels in human patients’ samples and HCC initiation or progression, respectively. Rap2 could mediate C3G pro-tumorigenic effect, although other mechanisms are possible. The relationship between C3G gene mutations and a poor prognosis is also included. Lower panel shows the antagonist contribution of Epac1 and Epac2 proteins in ALF and other effects of Epac1/Rap1 in the partial hepatectomy response.
ALF: Alcoholic liver fibrosis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma.