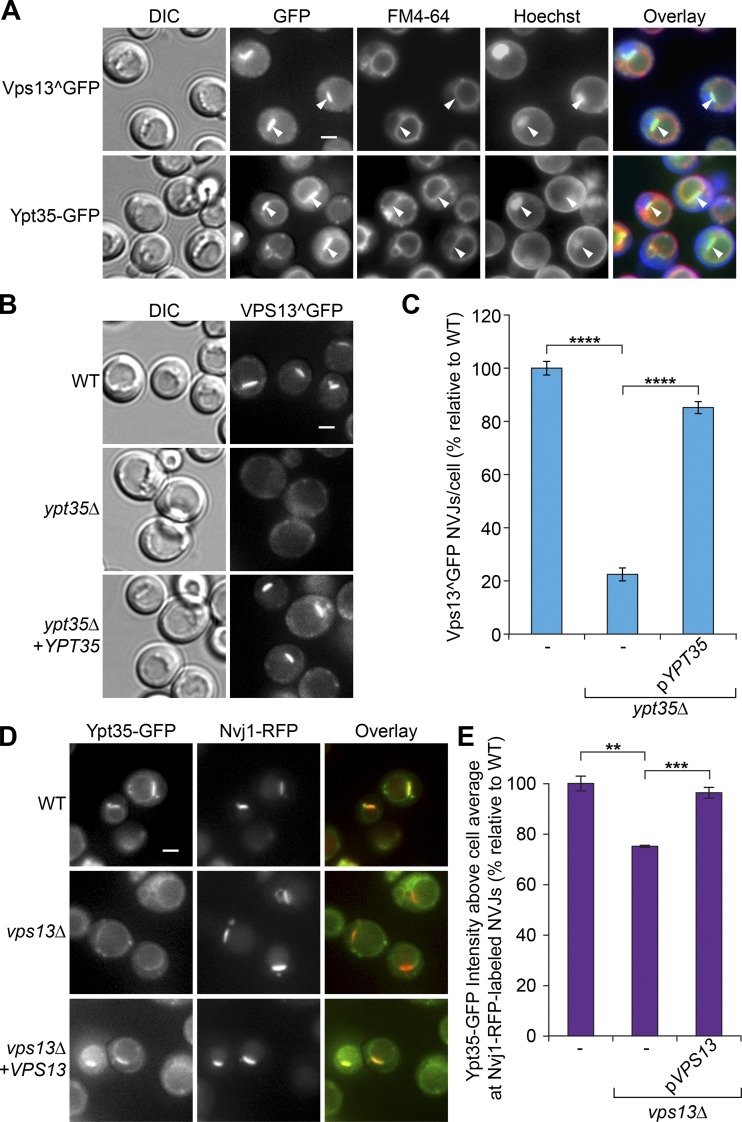
Figure 2.
Vps13 and Ypt35 are interdependent for recruitment to the NVJ. (A) Growth in acetate-based media shifts Vps13^GFP and Ypt35-GFP to the NVJ at the interface of the vacuole (FM4-64; red) and nucleus (Hoechst; blue). White arrowheads indicate NVJs. (B) Localization of Vps13^GFP to the NVJ in acetate-based media is Ypt35 dependent. (C) Quantitation of Vps13^GFP-labeled NVJs. Two-tailed equal variance t test; n = 3, cells/strain/replicate ≥ 1,149; ****, P < 0.0001. DIC, differential interference contrast. (D) Ypt35 is dependent on Vps13 for localization to the NVJ, labeled in this figure with Nvj1-RFP, in acetate-based media. (E) Quantitation of the average Ypt35-GFP intensity at Nvj1-RFP–marked NVJs relative to the cell background. Two-tailed equal variance t test; n = 3, cells/strain/replicate ≥ 1,672; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Bars, 2 µm. Error bars indicate SEM.