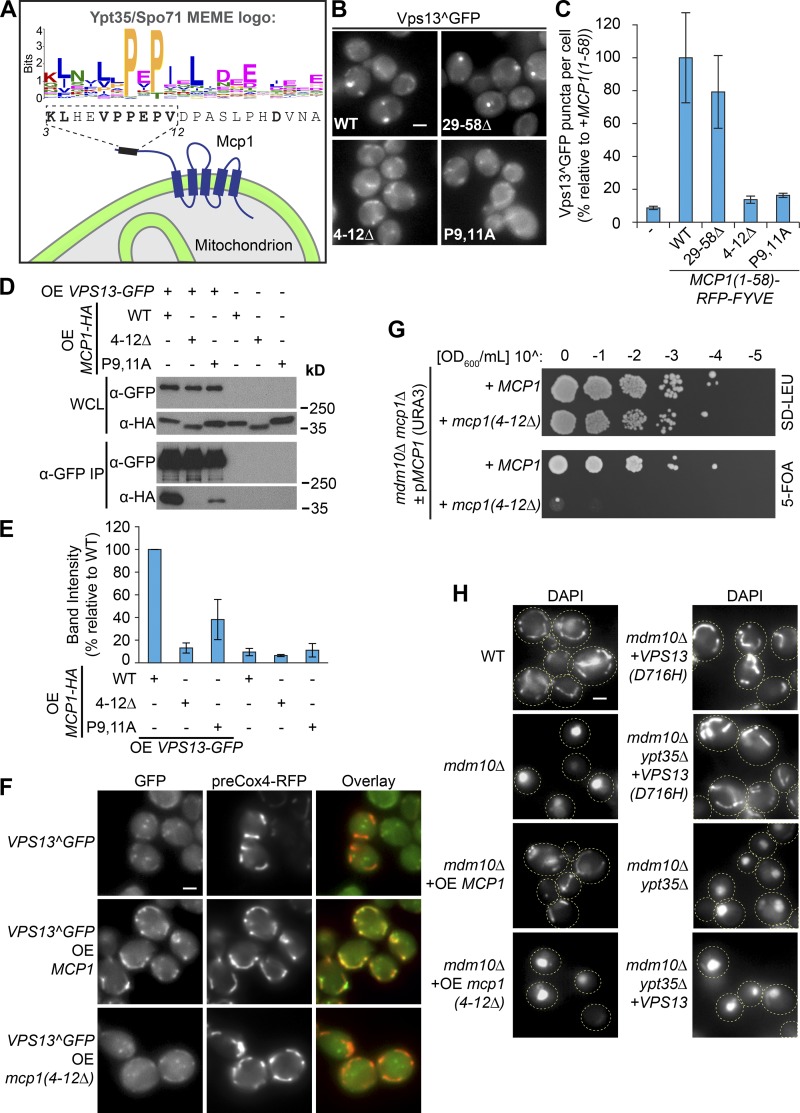
Figure 6.
Mcp1 is a mitochondrial PxP motif–containing Vps13 adaptor that interacts with Vps13 to suppress ERMES mutants. (A) Schematic of Mcp1 highlighting a putative PxP interaction motif identified by FIMO by using a MEME motif generated from Ypt35 and Spo71 homologues. (B) Mutation of the motif (4–12Δ, P9,11A) blocked the ability of the Mcp1(1–58)-RFP-FYVE chimera to induce Vps13^GFP puncta in a ypt35 strain. (C) Quantitation of Vps13^GFP puncta per cell; n = 3, cells/strain/replicate ≥ 1,410. (D) The motif is required for coprecipitation of Vps13 and Mcp1. Vps13-GFP and WT and mutant forms of Mcp1-HA were overexpressed (OE) from the ADH1 promoter. IP, immunoprecipitation; WCL, whole-cell lysate. (E) Densitometry of D; n = 3. (F) The interaction between ADH1pr-driven overexpression of WT Mcp1 but not Mcp1 lacking the PxP motif recruits Vps13^GFP to mitochondria marked by preCox4-RFP (red). (G) Loss of the Mcp1 PxP motif is synthetic lethal with mdm10Δ. (H) Overexpression of WT but not mutant Mcp1suppresses the mitochondrial morphology defect of a strain lacking the ERMES subunit Mdm10. In contrast, loss of YPT35 does not rescue the mdm10Δ mitochondrial morphology defect with or without expression of VPS13 from two copies of the gene, nor does it block rescue by the dominant suppressor Vps13(D716H). DAPI was used as a mitochondrial marker. Bars, 2 µm. Error bars indicate SEM.