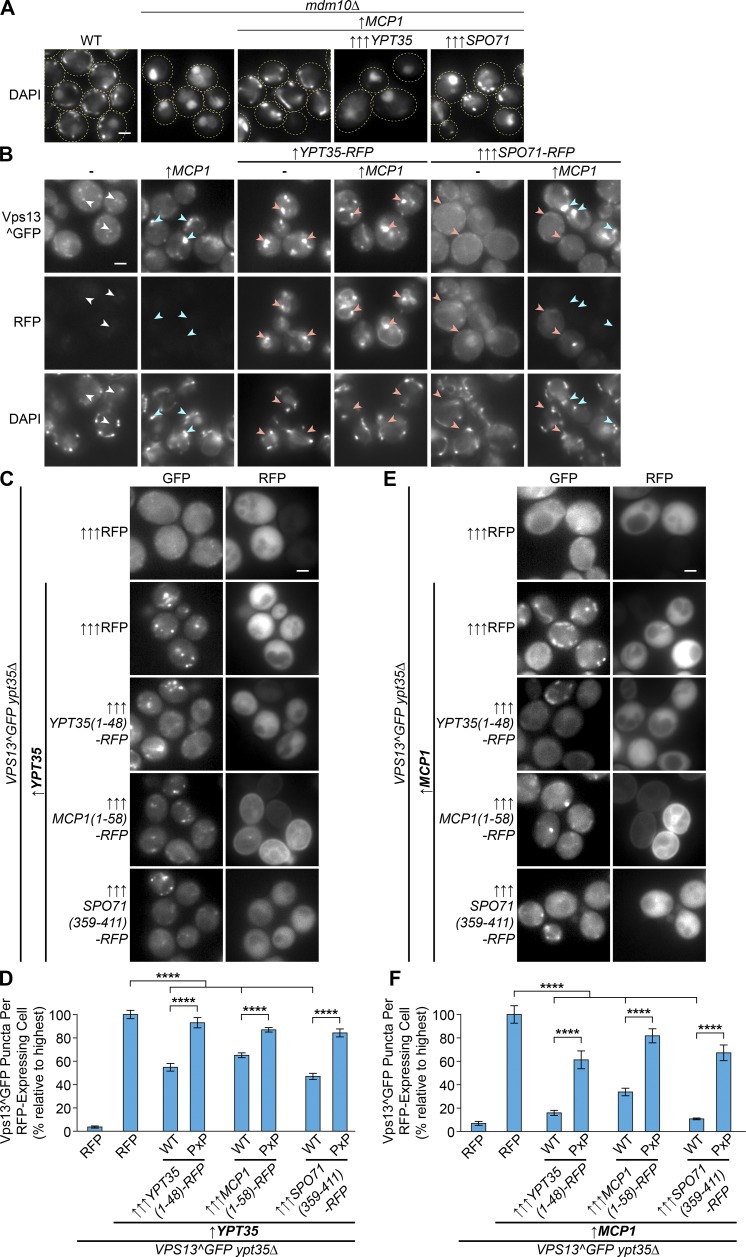
Figure 7.
Vps13 adaptors compete to recruit Vps13 to different membranes. (A) Suppression of the mdm10Δ mitochondrial morphology defect by moderately overexpressed Mcp1 (driven by the ADH1 promoter; ↑) is partially blocked by strong overexpression of Spo71 (driven by the TEF1 promoter; ↑↑↑) and completely blocked by strong overexpression of Ypt35 (driven by the GPD1 promoter; ↑↑↑). (B) High levels of Spo71-RFP or Ypt35-RFP block the Mcp1-dependent mitochondrial targeting of Vps13^GFP, which is instead relocalized to the plasma membrane or to endosomes, respectively. DAPI (blue) marks mitochondria. Arrowheads indicate Vps13^GFP colocalization with RFP (red), mitochondria (blue), or neither (white). (C) Vps13^GFP recruitment to puncta by YPT35 (ADH1pr; ↑) is reduced by highly expressed (TEF1pr; ↑↑↑) soluble RFP chimeras with the PxP motif–containing regions of Ypt35, Mcp1, or Spo71. (D) Quantitation of Ypt35-induced Vps13^GFP puncta in RFP-expressing cells shows a significant PxP-dependent reduction of puncta when the soluble chimeras are expressed. Unpaired one-way ANOVA: n = 5, ≥890 cells/strain/replicate; P < 0.0001 overall; Holm-Sidak's multiple comparisons test, ****, P < 0.0001. (E) Vps13^GFP recruitment to puncta by moderately overexpressed MCP1 (ADH1pr; ↑) is similarly reduced by strong overexpression (TEF1pr; ↑↑↑) of soluble RFP chimeras with the PxP motif–containing regions of Ypt35, Mcp1, or Spo71. (F) Quantitation of the Mcp1-induced Vps13^GFP puncta in RFP-expressing cells shows a significant PxP-dependent reduction of puncta when the soluble chimeras are expressed. Unpaired one-way ANOVA: n = 5, ≥719 cells/strain/replicate; P < 0.0001 overall; Holm-Sidak's multiple comparisons test, ****, P < 0.0001. Error bars indicate SEM. Bars, 2 µm.