Figure 6. In vivo DON administration reduces AML.
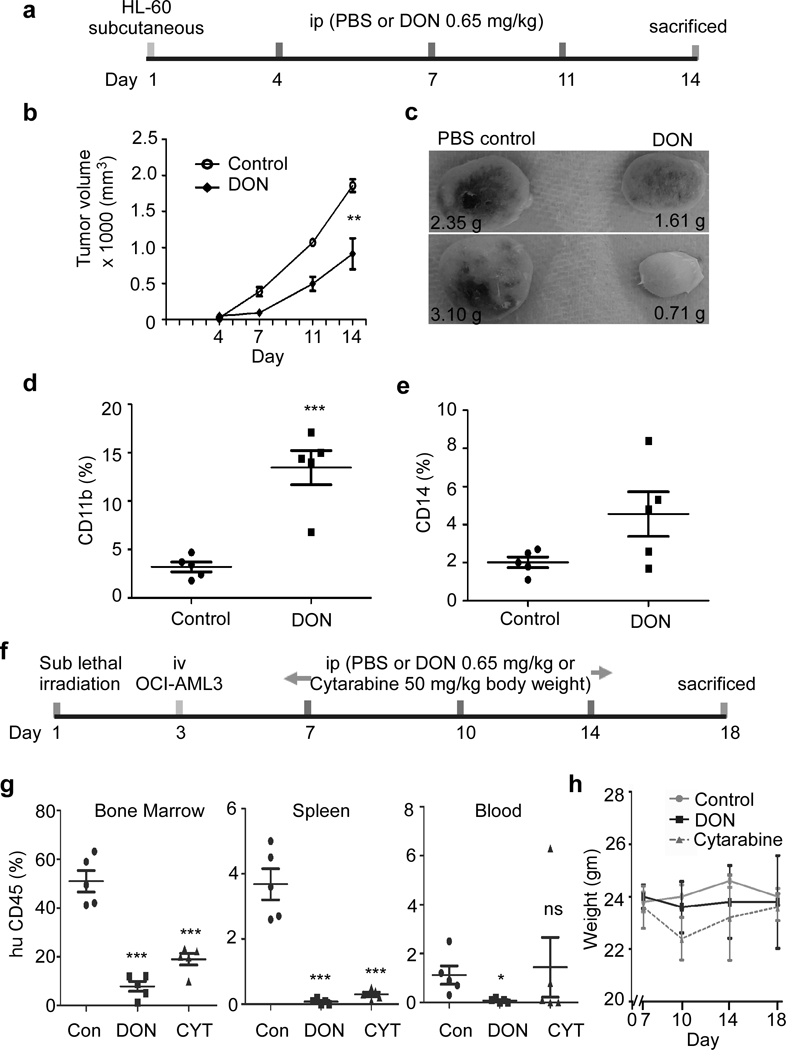
(a) Schematic representation of in vivo administration of DON or PBS in HL-60 based AML mice xenograft model. NSG mice were sub-cutaneous injected with HL-60 cells to generate solid AML mice xenograft model, followed by i.p. injection treatment as shown. (b) Tumor volume was monitored on day 4, 7, 11 and 14. (c) Representative image of harvested tumor is shown from control and DON treated mice group at day 14. Number indicates the weight of tumor in grams. Harvested tumors were analyzed for the presence of surface expression of differentiation marker (d) CD11b and (e) CD14. (f) Schematic representation of in vivo administration of DON/ cytarabine/ PBS in OCI-AML3 based AML xenograft mice model. Sub-lethally irradiated NSG mice were i.v. injected with OCI-AML3 cells to generate liquid AML xenograft mice model, followed by i.p. injection treatment as shown. (g) Bone marrow, spleen and blood cells isolated from indicated experimental groups were analyzed for the presence of human CD45 surface expression. Control group was i.p. injected with PBS and treated group was i.p. injected with DON (0.65 mg/kg). (h) Weight profile of animals from different experimental group during treatment regime at indicated days in AML mice model. N=5; Statistical significance was calculated using unpaired Student’s t-test. ns= not significant, *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
