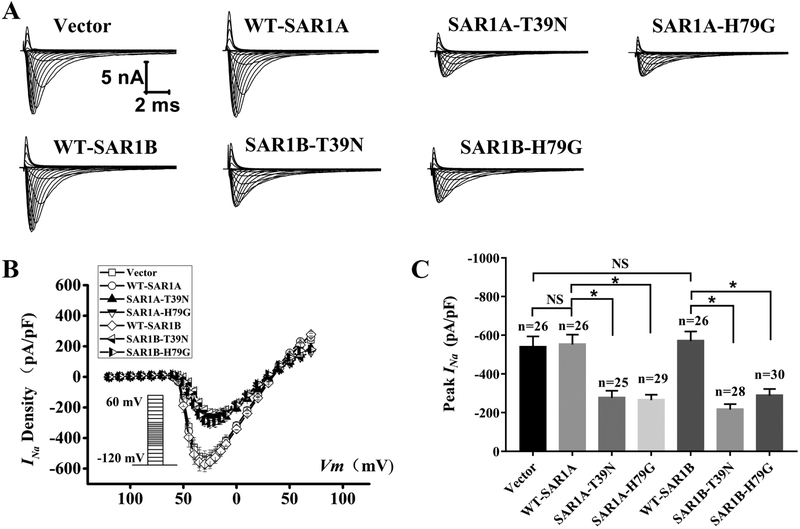
Fig. 4.
Mutant SAR1A and SAR1B GTPases with dominant negative mutations T39N and H79G decrease INa in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. (A) Representative whole-cell sodium current traces recorded from neonatal rat cardiomyocytes transfected with the empty vector control or expression plasmids for wild type (WT) SAR1A-Flag, SAR1A:H79G-Flag, WT-SAR1B-Flag. SAR1B:T39N-Flag or SAR1B:H79G-Flag, respectively. (B) The relationship between the average current density (current normalized to cell capacitance) and voltage. The voltage clamp protocol was shown in the inset. (C) The relative peak sodium current density at −30 mV among different treatment groups. Current densities (pA/pF) were −538.63±55.99 (n=26 cells) for the empty vector control, −276.64±36.80 (n=25 cells) for T39N-SAR1A-Flag, −265.22±27.91 (n=29 cells) for H79G-SAR1A-Flag, −552.17±51.53 (n=26 cells) for WT-SAR1A-Flag, −216.39±28.29 (n=28 cells) for SAR1B:T39N-Flag, −288.51±34.55 (n=30 cells) for SAR1B:H79G-Flag, and −570.23 ± 49.88 (n=26 cells) for WT-SAR1B-Flag. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. NS, not significant; *P < 0.05.