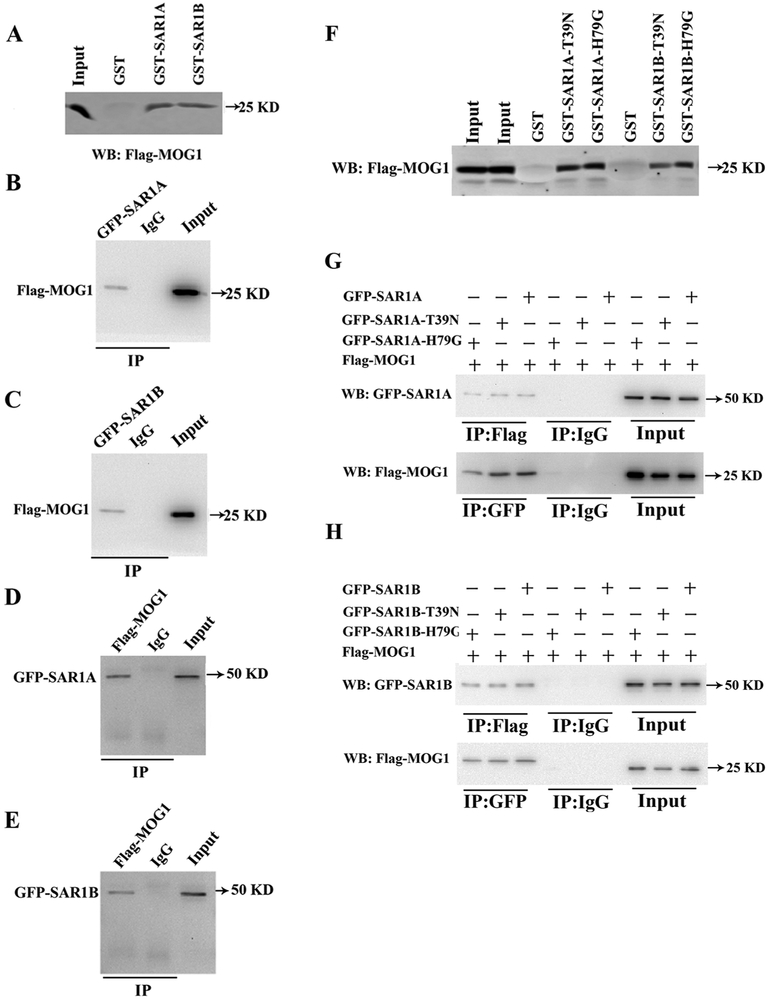
Fig. 7.
SAR1A and SAR1B interact with MOG1. (A) GST-pulldown analysis showed that Flag-MOG1 overexpressed in HEK293 cells was pulled down by either GST-SAR1A or GST-SAR1B, but not by GST. (B) Co-IP analysis showed that Flag-MOG1 in HEK293 cells was successfully precipitated by an anti-GFP antibody recognizing GFP-SAR1A, but bot by the control anti-mouse IgG. (C) Co-IP analysis showed that Flag-MOG1 in HEK293 cells was successfully precipitated by an anti-GFP antibody recognizing GFP-SAR1B, but bot by the control anti-mouse IgG. (D) Reciprocal Co-IP analysis showed that GFP-SAR1A in HEK293 cells was successfully precipitated by an anti-FLAG antibody recognizing Flag-MOG1, but not by the control anti-rabbit IgG. (E) Reciprocal Co-IP analysis showed that GFP-SAR1B in HEK293 cells was successfully precipitated by an anti-FLAG antibody recognizing Flag-MOG1, but not by the control anti-rabbit IgG. (F) GST-pulldown analysis showed that Flag-MOG1 in HEK293 cells was successfully pulled down by GST-SAR1A:T39N, GST-SAR1A:H79G, GST-SAR1B:T39N or GST-SAR1B:H79G, but not GST alone. (G) Top image: Co-IP analysis showed that the anti-Flag antibody recognizing Flag-MOG1, but not the control anti-rabbit IgG, successfully precipitated GFP-SAR1A, GFP-SAR1A:T39N or GFP-SAR1A:H79G. Bottom image: Reciprocal Co-IP analysis showed that the anti-GFP antibody recognizing GFP-SAR1A, GFP-SAR1A:T39N or GFP-SAR1A:H79G, but not the anti-mouse IgG, successfully precipitated Flag-MOG1. (H) Top image: Co-IP analysis showed that the anti-Flag antibody recognizing Flag-MOG1, but not the control anti-rabbit IgG, successfully precipitated GFP-SAR1B, GFP-SAR1B:T39N or GFP-SAR1B:H79G. Bottom image: Reciprocal Co-IP analysis showed that anti-GFP antibody recognizing GFP-SAR1B, GFP-SAR1B:T39N or GFP-SAR1B:H79G, but not the control anti-rabbit IgG, successfully precipitated Flag-MOG1.