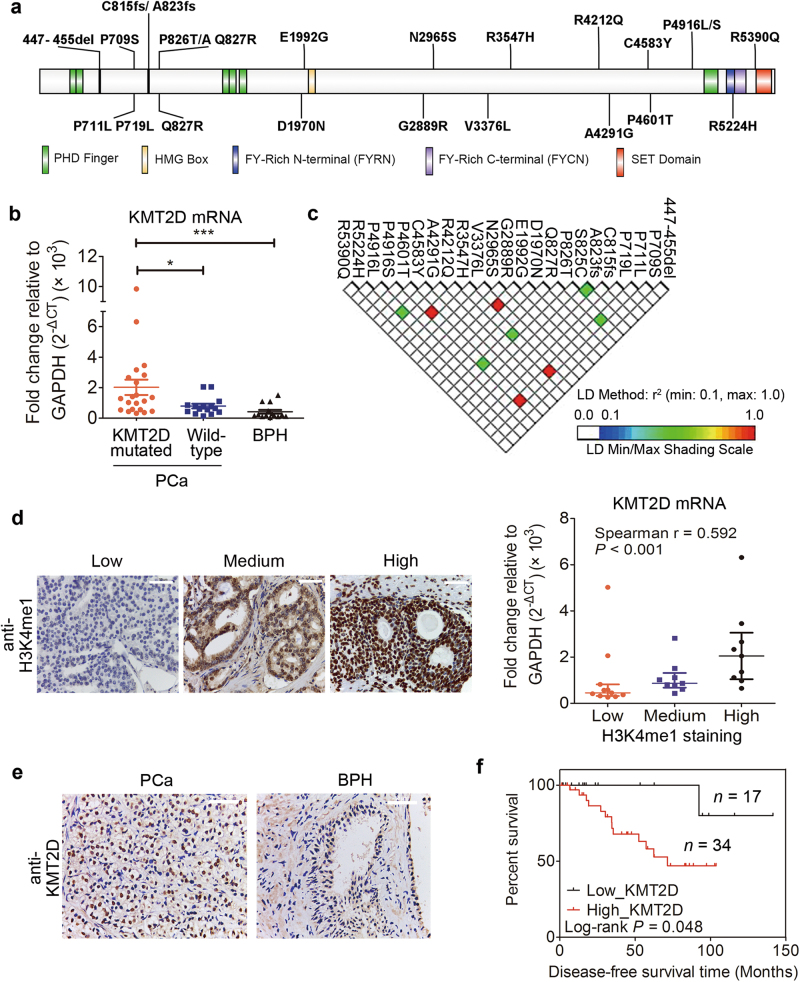
Fig. 2.
High expression of KMT2D in PCa is associated with recurrent mutations and leads to poor prognosis. a Schematic representation of KMT2D mutations detected in 63.04% (29/46) of prostate tumors. b mRNA expression of KMT2D in KMT2D mutated, wild-type cases, and benign prostate hyperplasia. c Linkage disequilibrium plot of KMT2D mutations in the protein-coding region. The LD plot is based on pairwise r 2 value. d KMT2D gene expression classified by H3K4me1 protein levels in PCa patients. Scale bars: 50 μm. e Representative images of immunohistochemistry staining against KMT2D in benign prostate hyperplasia (n = 3) and PCa samples (n = 51). Scale bars: 50 μm. f KM survival analysis of PCa patients based on protein expression of KMT2D (n = 51). Values are shown as median ± quartile