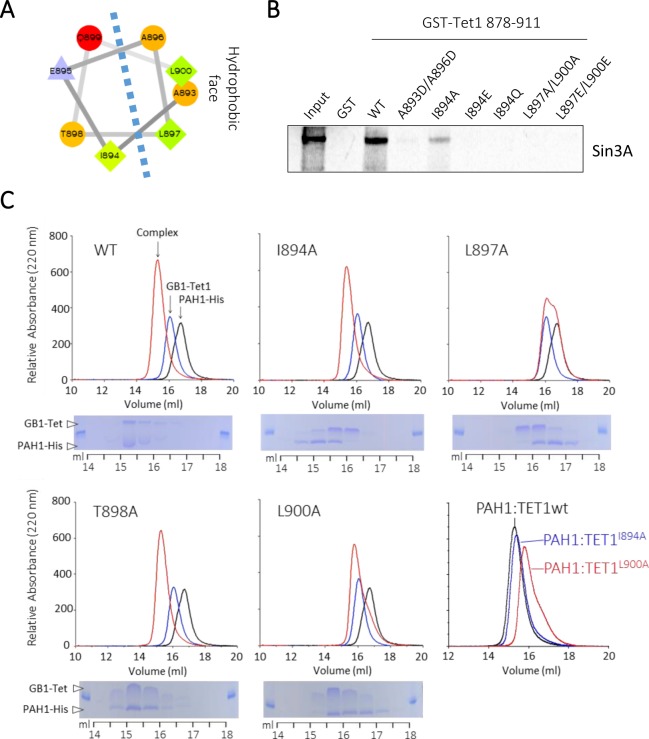
Figure 3.
The Tet1-SID forms an amphipathic helix with key hydrophobic residues required for interaction with Sin3A. (A) Helical wheel of the Tet1-SID residues 893–900 demonstrates hydrophilic and hydrophobic faces. (B) GST pulldown using GST-Tet1 878–911 wild-type and mutations, as indicated, with 35S-Met labelled Sin3A. This image is cropped, the uncropped version of the gel is shown in Supplementary Fig. S5C. (C) Column fractionation of purified GB1-Tet1 and PAH1-His (mixed at a 1:1 ratio) demonstrates their ability to form a binary-complex in solution, which is dependent on the presence of key hydrophobic residues.