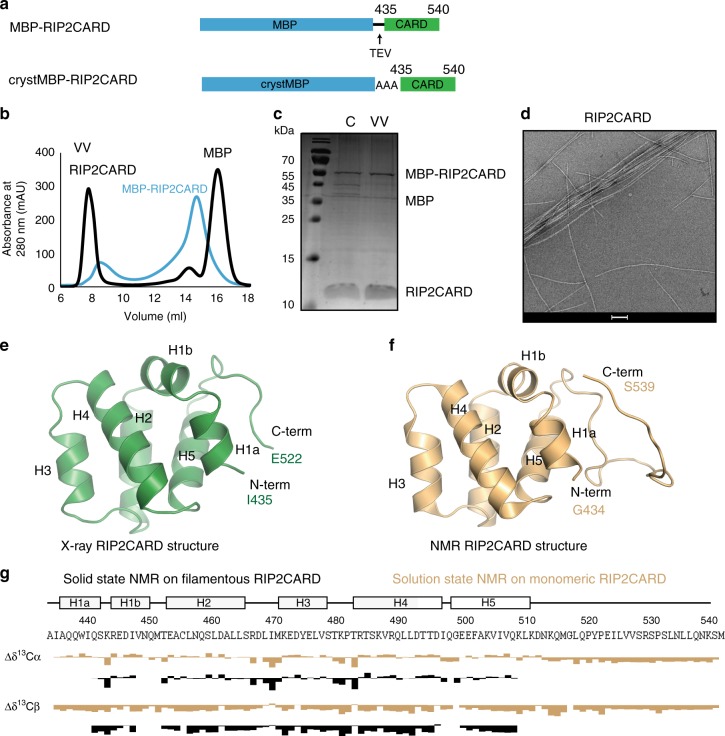
Fig. 3.
Structure of monomeric RIP2CARD. a Domain organization of MBP-RIP2CARD constructs used for expression and purification of recombinant RIP2CARD from E. coli Rosetta 2. MBP-RIP2CARD was used for characterising the polymerization ability of the CARD domain and for NMR experiments. CrystMBP-RIP2CARD was used for crystallization. b Typical size exclusion chromatography profiles of RIP2CARD purification showing both tagged (blue) and tag-free RIP2CARD (black). c 17 % SDS-PAGE showing typical sample obtained from RIP2CARD purification. The SDS-PAGE indicates that tag cleavage by TEV is incomplete. d Negative-stain electron micrograph of RIP2CARD VV. Scale bar is 100 nm. e Ribbon diagram of the RIP2CARD crystal structure reported in this paper f Ribbon diagram of the solution NMR structure of RIP2CARD (PDB: 2N7Z). g Comparison of secondary chemical shifts of RIP2CARD as a monomer in solution (yellow; BMRB entry: 25828) and in the filament, determined by proton-detected solid-state NMR (black). Experimental 13Cα and 13Cβ chemical shifts were subtracted from the respective random coil values for each amino acid type (ΔδCα, ΔδCβ)79,80. C: sample after tag cleavage as loaded on size-exclusion chromatography, VV: size exclusion chromatography void volume