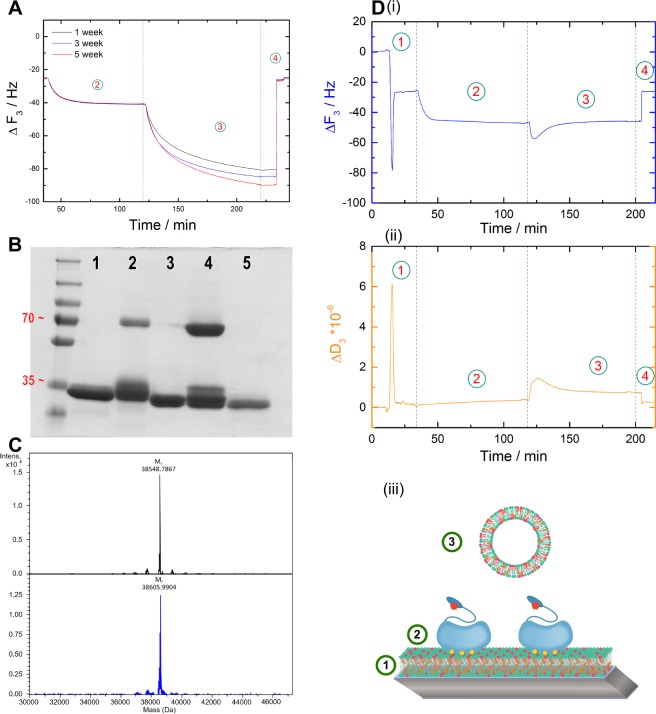
Figure 4.
Disulfide-based dimerization of AnxA2 affects membrane bridging/linking. (A) Frequency and dissipation shifts monitored in the QCM-D setup depicted in Fig. 1 that are induced by WT AnxA2 following incubation of the protein at non-reducing conditions for different periods of time [week: 1 (black), 3 (blue) and 5 (red)]. (B) SDS-PAGE analysis of different AnxA2 derivates under non-reducing conditions: 1, alkylated WT AnxA2; 2, WT AnxA2 (oxidation state after 1 week); 3, AnxA2 Δ32; 4, WT AnxA2 (oxidation state after 5 weeks); 5, AnxA2 Δ14. PageRuler™ Plus Prestained Protein Ladder was used as a molecular weight marker. (C) Mass analyses of non-modified WT AnxA2 (black graph) and the alkylated derivative (blue graph). (D) Time-resolved frequency (i) and dissipation (ii) monitoring of the reversible, Ca2+ dependent binding of alkylated AnxA2. A model representing the respective experimental setup is shown below the QCM-D recordings (iii). Shown are representative examples of a typical experiment carried out n = 8 independent times with two different protein batches and vesicle preparations.