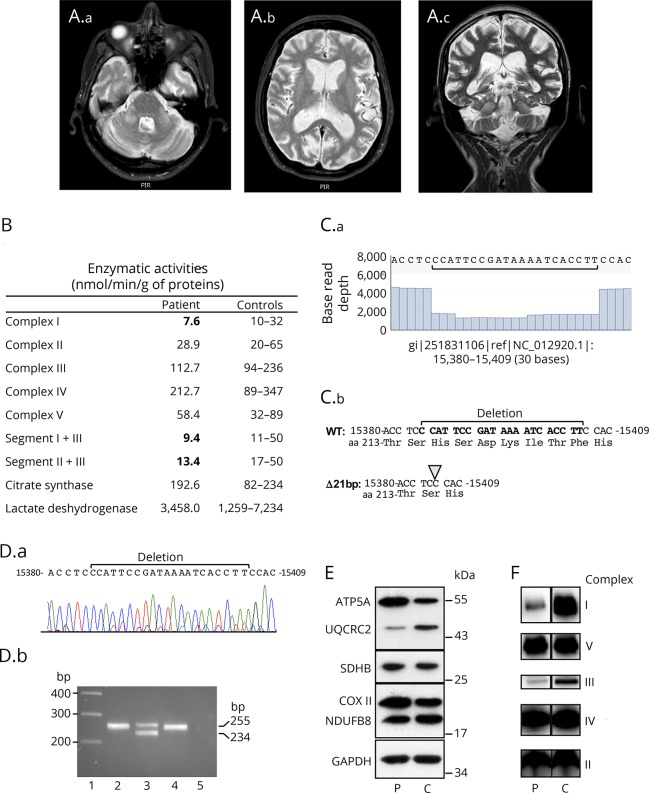
Figure. Brain MRI and characterization of the 21-bp MT-CYB deletion.
(A) Brain MRI. Axial T2-weighted (A.a) and coronal T2-weighted fast spin-echo (FSE) (A.c) MRI showing bilateral symmetrical hyperintensity of middle cerebellar peduncles. Axial T2-weighted (A.b) and coronal T2-weighted FSE (A.c) showing severe cortical and subcortical cerebral atrophy and mild cerebellar atrophy. (B) Mitochondrial respiratory enzyme activities of muscle from the patient and controls. (C.a) Read coverage analysis from nucleotide 15380 to 15409 showing the base read depth of each nucleotide. (C.b) Sequence from nucleotide 15380 with deduced amino acid sequence showing the 21-bp deletion. (D.a) Sanger sequence chromatogram from patient's muscle. (D.b) PCR products separated on a 2% agarose gel obtained with primers 15238-forward (5′-CTGAGGAGGCTACTCAGTAG-3′) and 15493-reverse (5′-GAGGTCTGGTGAGAATAGTGT-3′) that encompass the 21-bp deletion. PCR was performed on genomic DNA extracted from patient's tissues (blood, lane 2; muscle, lane 3) and blood of a control (lane 4). The wild-type and deleted amplicons are 255- and 234-bp, respectively. Lane 1: molecular weight marker 1 kb Plus (ThermoFisher Scientific), lane 5: no template negative PCR control. (E) Western-blot analysis from equal amounts (10 μg) of muscle homogenates of patient (P) and control (C) using oxidative phosphorylation system antibodies cocktail detecting NDUFB8 (complex I), SDHB (complex II), UQCRC2 (complex III), COXII (complex IV), ATP5A (complex V), and anti-GAPDH antibody for loading control. (F) Blue native polyacrylamide gel analysis from muscle homogenates of patient (P) and control (C). Equal amounts (15 μg) of proteins were separated on a 4%–13% acrylamide gradient gel and electroblotted onto a polyvinylidene fluoride membrane prior to incubation with specific antibodies against GRIM19 (subunit of complex I), SDHA (subunit of complex II), UQCRC2 (subunit of complex III), MTCO1 (subunit of complex IV), and ATP5A (subunit of complex V).