FIG 1.
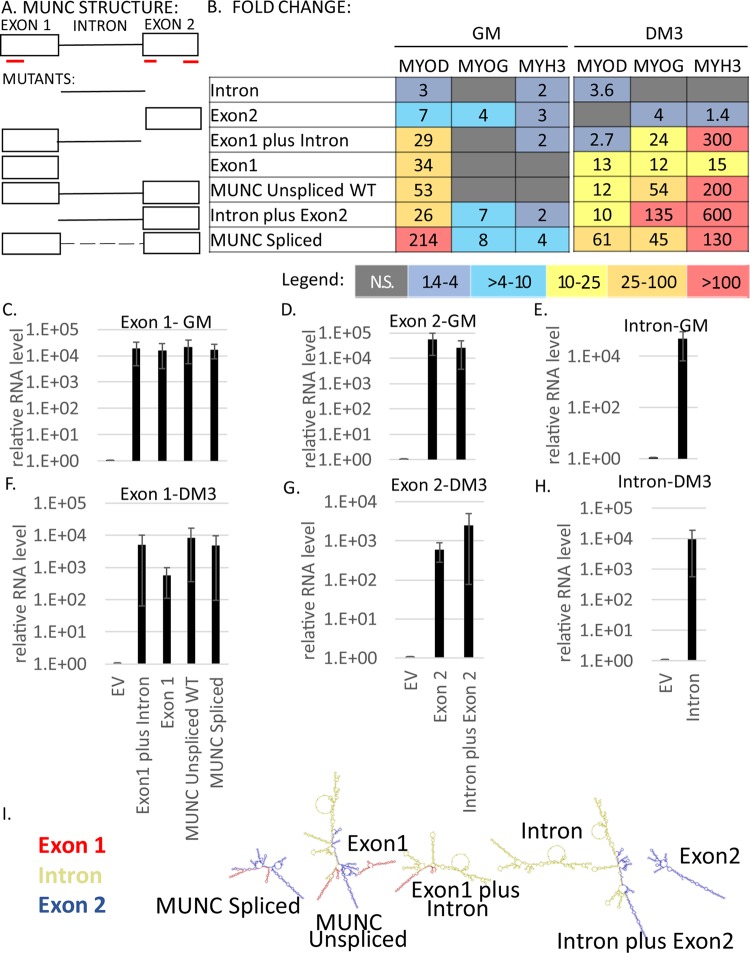
MUNC has at least two domains important for its function. (A) Schematic illustrating MUNC structure. The red lines indicate three potential micropeptides coded by MUNC spliced sequence: two of 20 amino acids and one of 60 amino acids. The micropeptides were defined using a translation tool (http://web.expasy.org/translate/). (B) Heat maps showing summaries of qRT-PCR analyses of C2C12 mutant cells stably overexpressing different truncated MUNC sequences. Levels of myogenic factor transcripts were measured in three biological runs and normalized to the GAPDH (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) level and to control cells under each condition, and mean values were calculated. The colors used in the heat maps correspond to fold changes according to the legend. N.S., not significant. Analysis of proliferating cells and differentiating cells. (C to H) qRT-PCR analysis of mutant cells overexpressing truncated MUNC sequences showing levels of different parts of the transcript (exon 1, intron, and exon 2) in GM (C to E) and in DM3 (F to H). The data were normalized to GAPDH and to control cells transfected with an EV. The values represent three biological replicates and are presented as means and standard errors of the mean (SEM). (I) Predicted structures of different mutants of MUNC generated using the Forna RNA prediction tool.