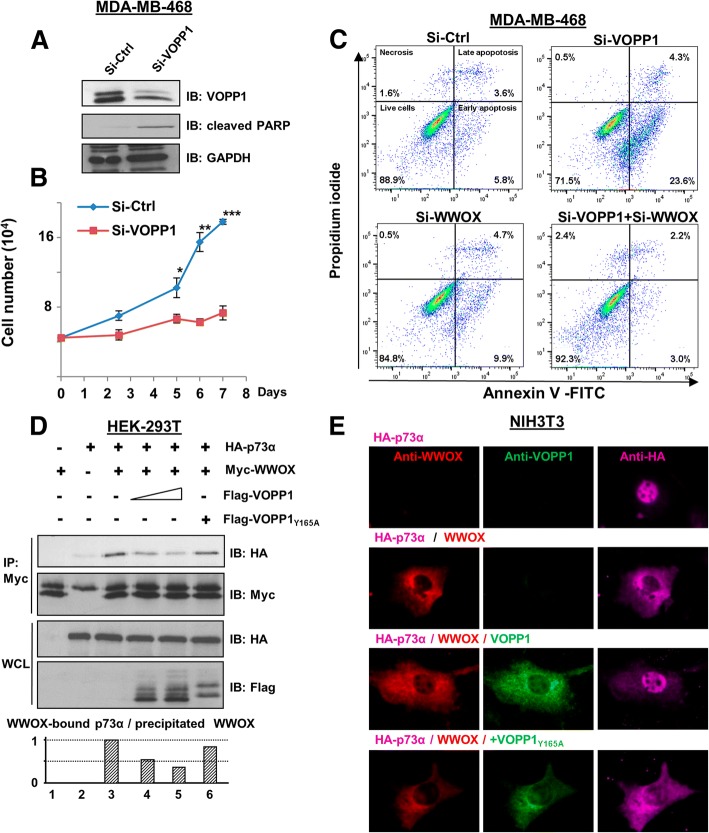
Fig. 4.
VOPP1 inhibits WWOX pro-apoptotic activity. a MD-MB-468 cells were transfected with control (Si-Ctrl) and VOPP1 siRNAs (Si-VOPP1) for 3 days. Cellular extracts were immunoblotted with anti-VOPP1, anti-cleaved PARP, and anti-GAPDH (loading control) antibodies. b An MTS assay was performed at times as indicated; cell numbers are expressed as mean + SEM of triplicates from a representative experiment. Student t test (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). c MD-MB-468 cells were transfected with control, VOPP1, and WWOX siRNAs as indicated. Three days later, cells were collected and the percentage of apoptotic cells was evaluated by flow cytometry. d HEK-293T cells were transfected with HA-p73α (0.5 μg), Myc-WWOX (0.5 μg), Flag-VOPP1 (0.5 or 1 μg), and Flag-VOPP1Y165A (1 μg) expression vectors as indicated. Co-immunoprecipitation results show a decreased level of the WWOX-p73 complex in the presence of ectopic VOPP1 but not VOPP1Y165A. e Cells were transfected with HA-p73α alone or in combination with WWOX, WWOX and VOPP1, or WWOX and VOPP1Y165A expression vectors as indicated. Twenty-four hours after transfection, cells were fixed, permeabilized, and immunostained with anti-WWOX, anti-VOPP1, and anti-HA antibodies followed by appropriate secondary fluor-conjugated antibodies. After immunostaining, cells were imaged with a fluorescence microscope and the images were overlaid (original magnification, × 100)