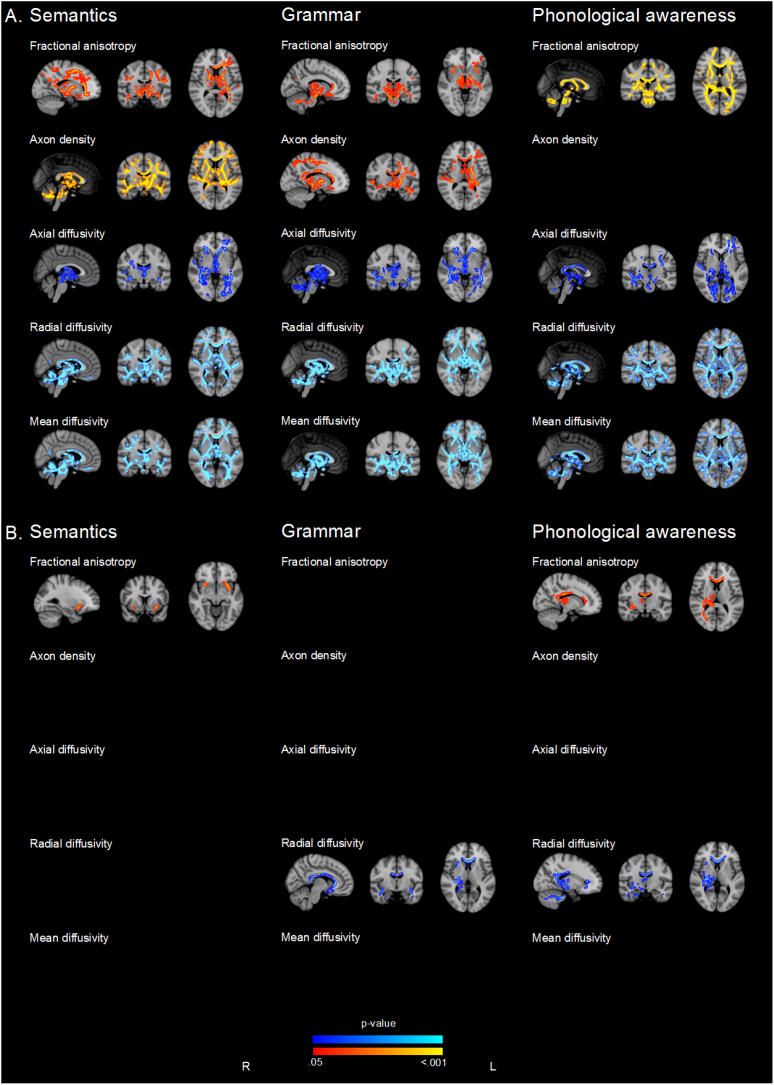
Fig. 2.
Regions where there is evidence (p < .05, family wise error rate corrected) of A. associations between white matter microstructure parameters and language when assessed in all children, corrected for age, sex, language spoken at home and parental education and B. associations between white matter microstructure parameters and language in children without major brain pathologies, very low IQ and lowest possible language score. P-values in red-yellow = positive correlations and dark to light blue = negative associations. P-value maps have been overlaid on the standard space (MNI152) T1-weighted image. Note, no image is shown when no voxels were identified at p < .05 family wise error rate-corrected. Analyses were not corrected for multiple comparisons across white matter microstructure parameters.