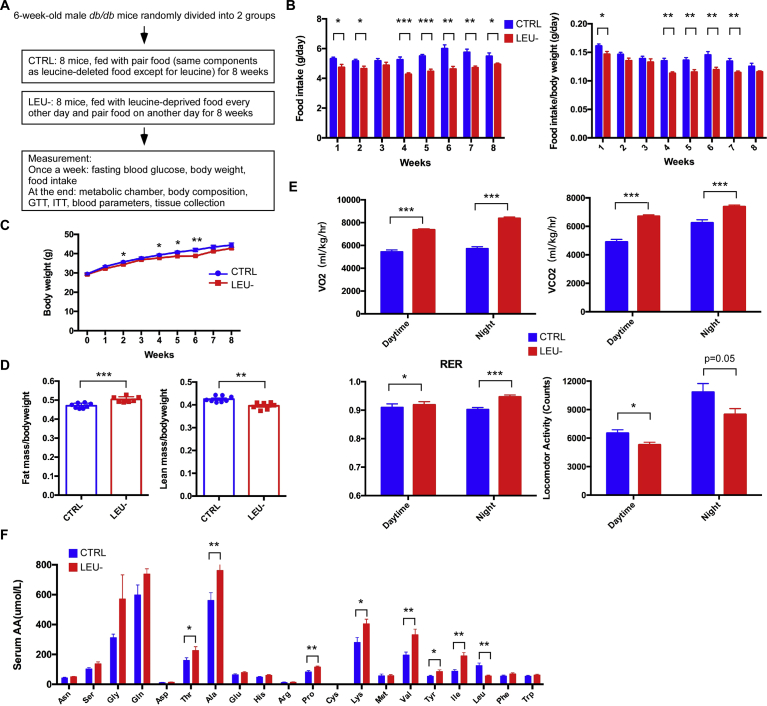
Fig. 1.
Intermittent leucine deprivation alters body composition, metabolic rate, physical activity, and blood amino acid levels in db/db mice. (A) Flowchart of the experiment. The db/db mice were divided into 2 groups. The control group (CTRL) was parallel-fed ad libitum. Another group was fed ad libitum with leucine-deprived food every other day (LEU-) groups (n = 8 mice/group). (B) Food intake of the mice. The adjusted food intake by body weight is shown on the right. (C) Body weight of the mice. (D) Quantification of fat mass and lean mass by MRI scan. (E) Analyses of the mice with metabolic chamber to quantitate O2 consumption, CO2 production, respiratory exchange ratio (RER), and X-locomotor activity. (F) Serum amino acid levels of the mice as detected by LC-MS/MS analysis. The mice were euthanized ad libitum on the control diet. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.