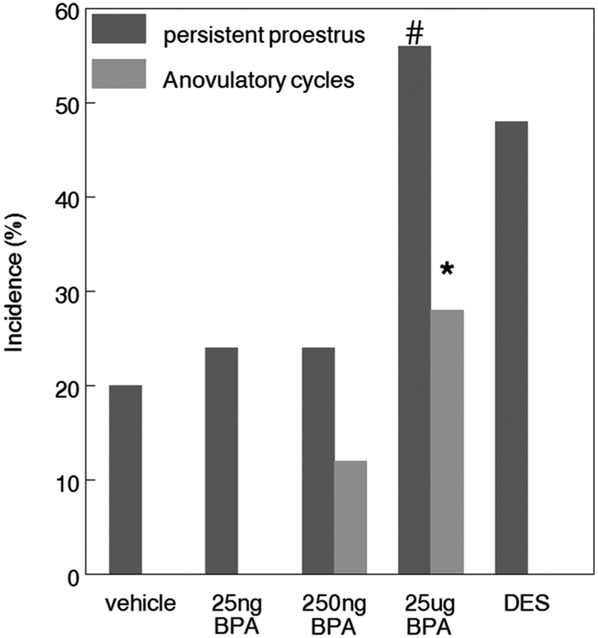
Fig. 3.
In utero BPA exposure resulted in a dose-dependent alteration in estrous cyclicity. By 6 months of age, females exposed to 25 μg BPA showed a significant increase in the incidence of anovulatory cycles assessed over a 14 day period compared to controls (Chi Sq * p < 0.05) In addition, the incidence of persistent proestrus is also increased but does not reach statistical significance, (# p=0.053) n = 17–21/treatment.