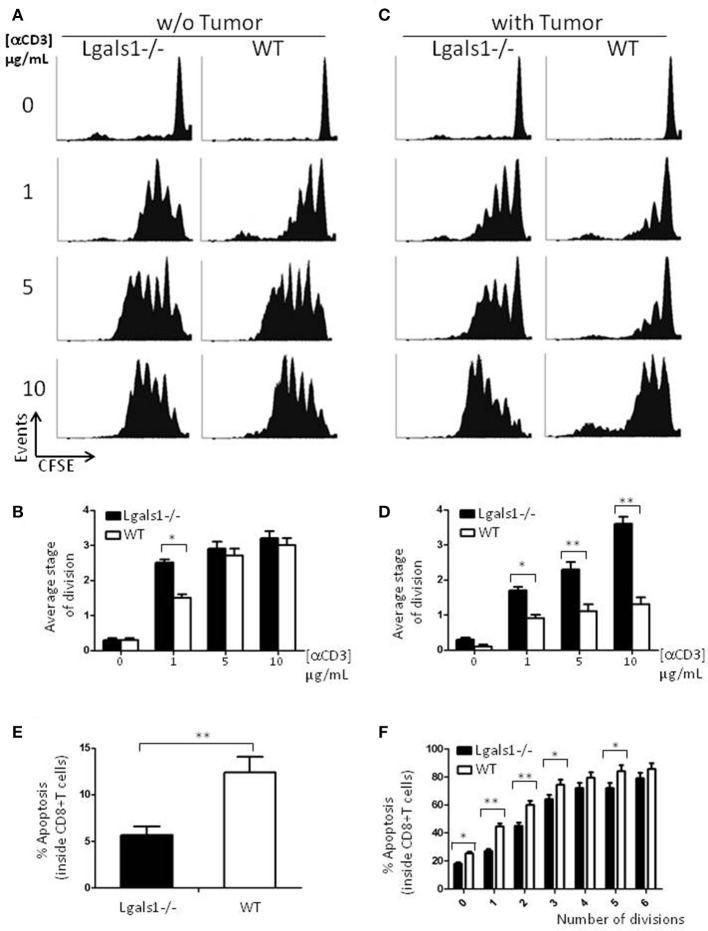
Figure 2.
Role of endogenous Galectin-1 in the proliferation and activation-induced cell death of CD8+ T cells. Proliferation rates of wild-type and Lgals1-/- CD8+ T lymphocytes are compared upon activation with different anti-CD3 concentrations in a 72 h proliferation assay. (A,B) In the absence of TRAMP-C1 tumor cells. (A) Representative CFSE dilution proliferative experience. (B) Graph bars indicating the average stage of division obtained from three independent experiences; White bars: wild-type cells; Black bars: Lgals1-/- cells (*p < 0.05, t-test). (C,D) In the presence of 1% TRAMP-C1 tumor cells. (C) Representative CFSE dilution proliferative experience. (D) Graph bars indicating the average stage of division obtained from three independent experiences; White bars: wild-type cells; Black bars: Lgals1-/- cells (*p < 0.05, t-test). (E) Role of endogenous Galectin-1 in the apoptosis of CD8+ T cells upon polyclonal activation in the presence of 1% TRAMP-C1 cells. Apoptosis rates of wild-type (n = 3) and Lgals1-/- (n = 3) lymphocytes are comparatively analyzed by Annexin V staining inside total CD8+ T cell gate (E) or inside each peak of division (CFSE) in the CD8+ T cell gate (F). White bars: wild-type cells; black bars: Lgals1-/- cells (*p < 0.05, t-test).