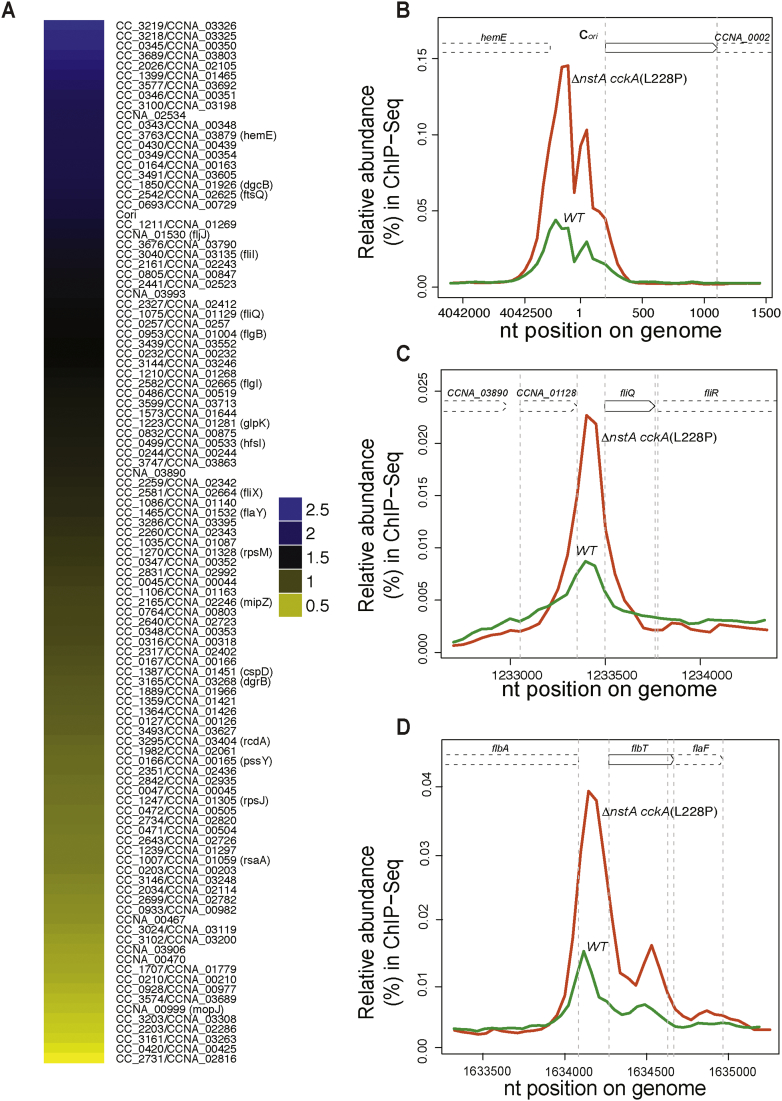
Fig. 3.
The CckA(L228P) mutation leads to differential DNA binding of CtrA. (A) Genome-wide comparative ChIP-Seq using polyclonal antibodies to CtrA, denoting the occupancy of CtrA on the chromatin of WTcckA vs ∆nstA cckA(L228P) mutant cells. The color key (log2 ratio) indicates the degree by which the occupancy of CtrA is varied, at the promoters of selected target genes, as a result of the CckA(L228P) substitution (see Supplementary Dataset 1 for the complete list of targets). Traces of the occupancy of CtrA at (B) the chromosomal origin of replication, Cori, (C) the promoter of fliQ and (D) the promoter of flbT. Fig. 3B–D were derived from the ChIP-Seq data and the traces of CtrA in the WT is denoted in green, and in the ∆nstA cckA(L228P) mutant is denoted in red. Also see Supplementary Fig. S4.