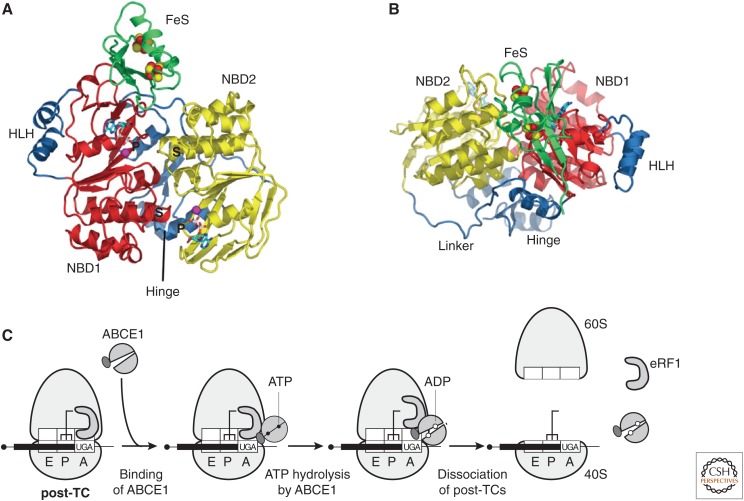
Figure 3.
Ribosome recycling in eukaryotes. (A,B) Ribbon representations of ABCE1 from Pyrococcus abyssi bound to ADP (protein data bank [PDB]: 3BK7). Top (A) and front (B) views, showing nucleotide-binding domain NBD1 (red), with its helix–loop–helix insertion (HLH), linked to NBD2 (yellow) by the hinge domain. The FeS domain includes two [4Fe-S] clusters (red and yellow spheres), and binds to the lateral opening of the nucleotide-binding cleft. Nucleotides bind to the two composite binding sites formed by P-loop/Walker A (“P”) and signature (S) motifs. (From Karcher et al. 2008; reprinted, with permission, from The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology © 2008.) (C) Model for ribosome recycling (Pisarev et al. 2010), in which ABCE1 binds to eRF1 on the post-termination complex (post-TC), and ATP hydrolysis leads to a power stroke that splits the post-termination ribosome, yielding a 60S subunit, eRF1, ABCE1, and a 40S subunit still bound to messenger RNA (mRNA) and deacylated transfer RNA (tRNA).