Figure 3.
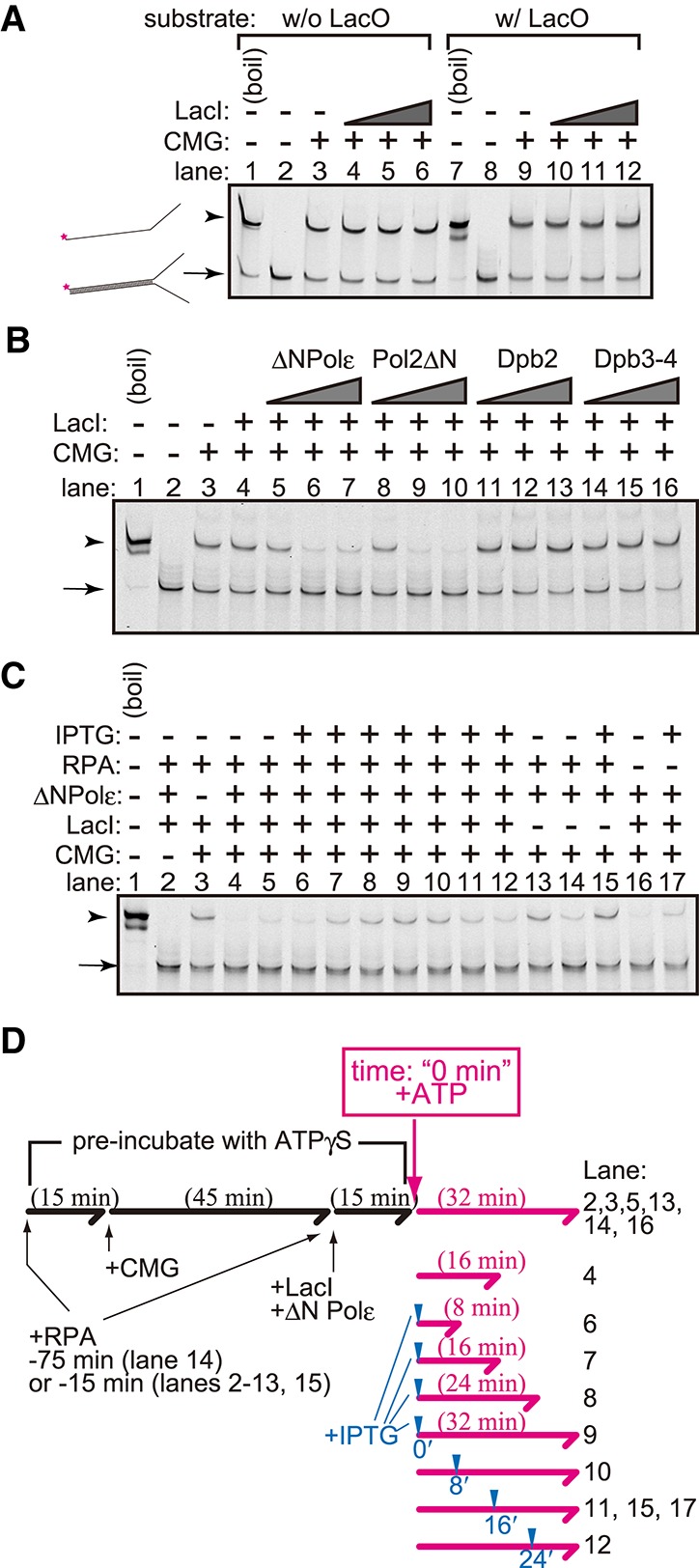
Helicase assay using a purified CMG complex. (A) The CMG helicase assay was performed using forked DNA with (lanes 7–12) or without (lanes 1–6) the LacO sequence as a substrate. CMG (200 fmol) was mixed with 2 fmol of the substrates and ATPγS in the presence (36, 72, and 144 fmol) or absence of LacI. ATP was added, and a helicase reaction was then performed in its presence. The reaction was stopped by adding EDTA and sarkosyl and was used for native PAGE analysis. DNA was detected by the infrared signal label located at the end of the forked substrate. (B) The CMG helicase assay was performed as shown in A, but 6, 18, and 54 fmol of the Polε–pol2ΔN complex (ΔNPolε), pol2ΔN, Dpb2, or the Dpb3–Dpb4 (Dpb3–4) complex was added. (C) The CMG helicase assay was performed as shown in A and B using 144 fmol of LacI, 54 fmol of the Polε–pol2ΔN complex (ΔNPolε), and 275 fmol of RPA. IPTG was added to the reaction at the final concentration of 10 mM at the time point indicated in D. (D) Flowchart of the helicase assay shown in C. The forked DNA substrates were preincubated with proteins in the presence of ATPγS for the indicated period (black lines and characters). The time point of the addition of IPTG and the incubation time after the addition of ATP are indicated by blue arrowheads and the lengths of the magenta arrows, respectively.
