Figure 1.
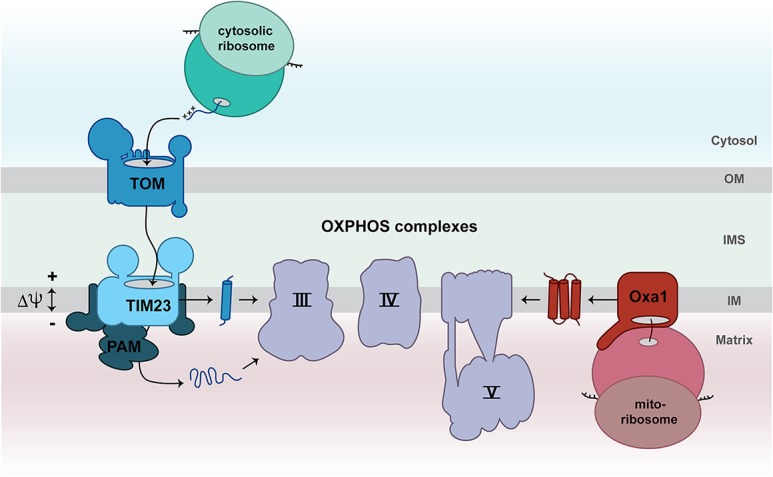
Biogenesis of mitochondrial respiratory chain subunits. The majority of nuclear-encoded subunits of the respiratory chain is synthesized by cytosolic ribosomes as precursors and imported into mitochondria via the translocase of the mitochondrial outer membrane (TOM complex) and the presequence translocase (TIM23 complex). Transport into the mitochondrial matrix additionally requires the ATP-dependent activity of the presequence translocase-associated motor (PAM). The membrane potential (Δψ) across the inner membrane drives protein translocation via the presequence pathway. The OXA1 complex inserts mitochondrially encoded subunits into the inner membrane in a cotranslational manner. Finally, mitochondrially encoded and nuclear-encoded subunits assemble into functional respiratory chain complexes. (IM) Inner membrane; (IMS) intermembrane space; (OM) outer membrane.
