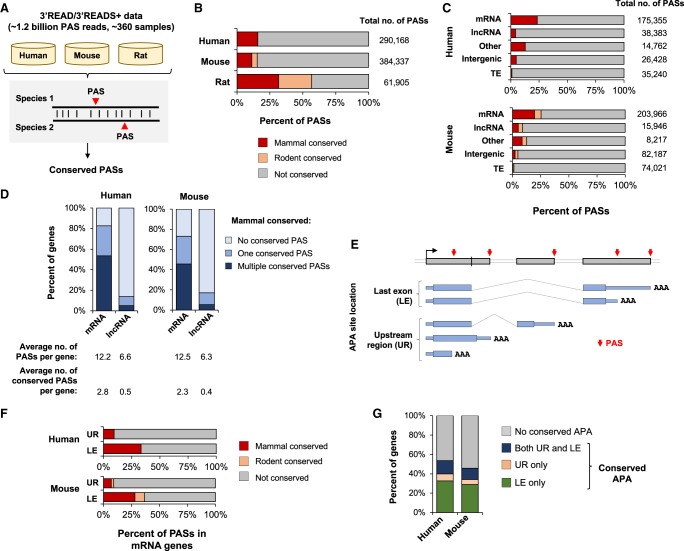
Figure 1.
Mapping and statistics of conserved PASs in mammals. (A) Mapping PASs in human, mouse, and rat genomes using 3′READS or 3′READS+ data, and identification of conserved PASs using the reciprocal best-match method. (B) Percentage of PASs conserved in human, mouse, and rat genomes. Two types of conservation are shown, i.e., conserved in mammals (human versus mouse or rat) and conserved in rodents only. Total number of PASs mapped for each species is shown. (C) Percentage of conserved PASs of different gene groups. The number of PASs in each group is indicated. The “other” group contains PASs from overlapping genes (on the same strand) and pseudogenes. (D) Percentage of mRNA or lncRNA genes with conserved PASs. The average number of PASs per gene (with or without conservation in mammals) is indicated. (E) APA sites in different loci of an mRNA gene. The sites are grouped into last exon (LE) or upstream region (UR). (F) Percentage of conserved UR and LE PASs of mRNA genes. (G) Percentage of genes with conserved APA sites in UR, LE, or both; UR APA conservation requires a gene to contain at least one conserved UR PAS, and LE APA conservation requires a gene to contain at least two conserved LE PASs.