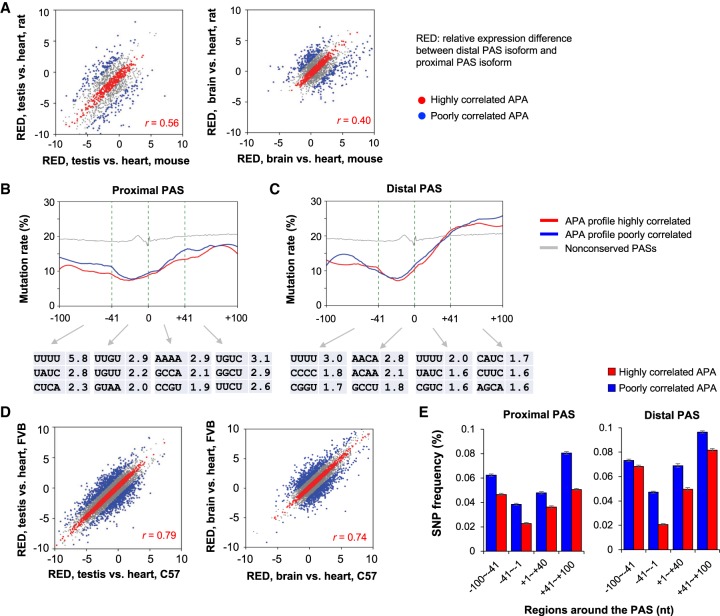
Figure 6.
Sequence variation leads to APA changes. (A) Correlation of APA profiles between mouse and rat. (Left) APA profile based on testis versus heart; (right) APA difference between brain and heart. APA difference was calculated as RED = Δlog2(distal PAS/proximal PAS), testis or brain versus heart. Genes in red have highly correlated APA events (middle 30% of genes based on REDmouse − REDrat), and those in blue have poorly correlated APA events (top and bottom 10% of genes based on REDmouse − REDrat). (B, top) Nucleotide mutation rate (percentage of mutations at each position per gene) around the conserved proximal PAS based on mouse and rat comparison. Red and blue lines are genes with highly correlated and poorly correlated APA profiles from A, respectively. (Bottom) Top three enriched tetramers in mutated sequences of genes with poorly correlated APA events. −log10(P) values (Fisher's exact test) are shown. (C) As in B, except that data for conserved distal PASs are shown. (D) As in A, except that comparisons are based on two mouse strains, C57BL/6J (C57) and FVB/JN (FVB). (E) SNP frequencies around conserved proximal and distal PASs of genes with highly correlated (red) or poorly correlated APA events (blue) between two mouse strains.