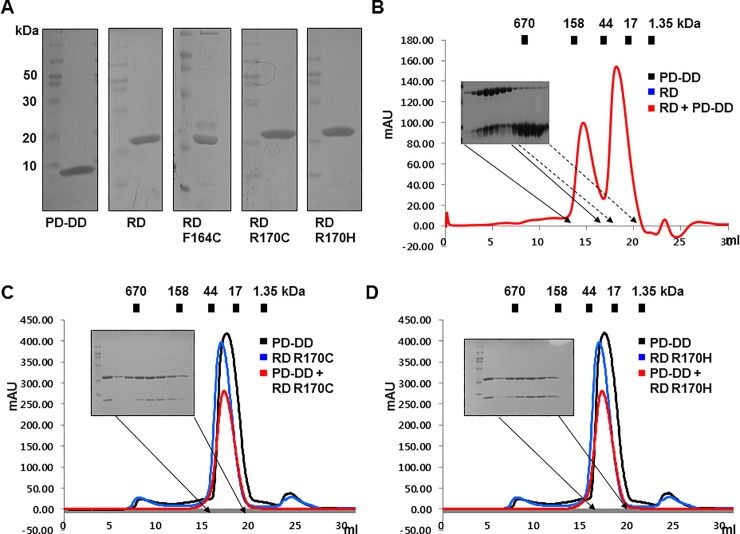
Fig 3. Full-length RAIDD-TLIS variants, R170C and R170H, failed to interact with PIDD DD, while another variant, F164C, lost its stability.
A. Purification of full-length RAIDD, PIDD DD, and three full-length RAIDD-TLIS variants. Finally, purified protein samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE, and protein bands were detected by Coomassie blue staining. The migration of size markers is shown on the left side. PD-DD and RD indicate PIDD DD and full-length RAIDD, respectively. B. Results of size exclusion chromatography showed that wild-type RAIDD formed a stable complex with PIDD DD. Red peak fractions produced by RAIDD:PIDD DD complex that eluted at around 12–13 ml were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. C and D. Results of size exclusion chromatography of the mixture of PIDD DD and the RD R170C variant (C) or RD R170H variant (D). Red peak fractions from the mixtures of PIDD DD and two variants of RAIDD were subjected to SDS-PAGE and visualized by Coomassie staining.