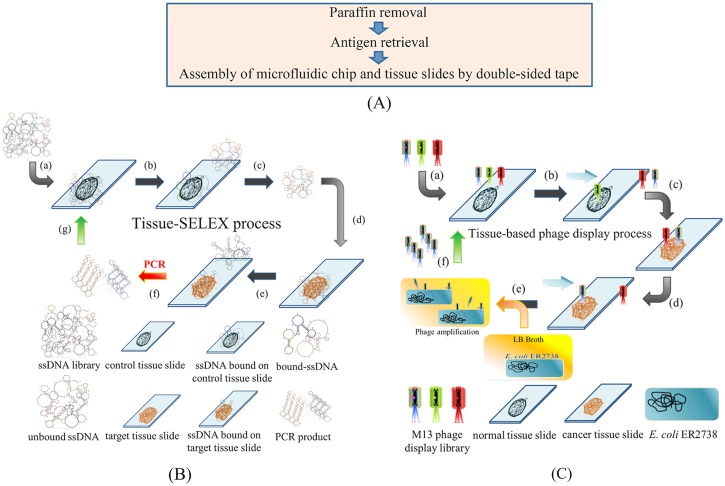
FIG. 1.
Working principles of the tissue-based cancer biomarker screening process. (a) The paraffin layer was removed, and tissue antigens were boiled in citrate buffer. After antigen retrieval, tissue slides were attached to the microfluidic system and they were assembled with a laser-engraved, double-sided tape. (b) The tissue-SELEX process: (a) the ssDNA library was first incubated with normal ovarian tissues (negative selection); (b) unbound ssDNA were separated, and [(c) and (d)] incubated with ovarian cancer tissues (positive selection). (e) Aptamer candidates bound to cancer tissues, and unbound ssDNA were washed away. (f) The bound aptamer candidates were PCR amplified, and (g) PCR products were used in the next round of tissue-SELEX. (c) In the phage display process, (a) an M13 phage library was incubated with normal tissues (negative selection). [(b) and (c)] Then, unbound phages were incubated with cancer tissues (positive selection), and (d) unbound phases were washed away. (e) Positive phages were amplified in E. coli. (f) These amplified phage candidates were used in the next round of phage display.