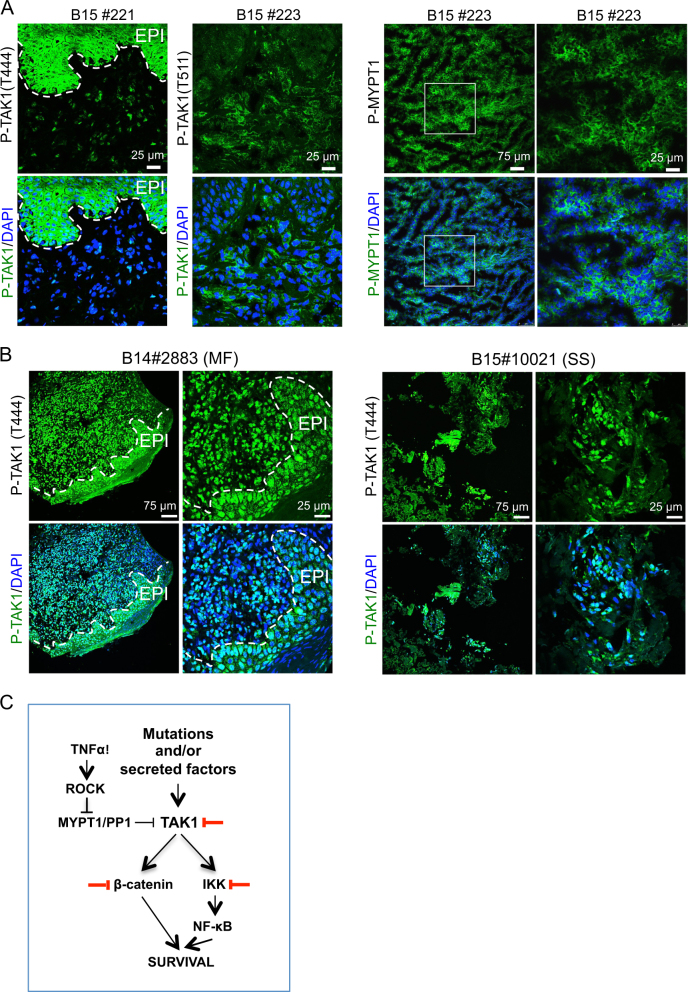
Fig. 6.
The MYPT1-TAK1 pathway is activated in human cutaneous T-cell lymphomas. a Immunofluorescence analysis of P-TAK1 (left panels) and P-MYPT1 (right panels) in human primary CTCL frozen samples. Representative images from eight different samples analyzed. b Immunohistochemistry analysis of P-TAK1 (T444) in two representative (1 MF and 1 SS) paraffin-embedded human primary CTCL samples. Dashed lines in A and B delineate the boundary between epidermal cells (EPI) and the dermis where lymphoma cells are located. c Model for TAK1 inhibition as therapy for CTCL. Based on our data, NF-κB is activated in CTCL, but partially counteracted by the PP1/MYPT1 phosphatase activity. Cytokines (TNFα) or other factors promote a ROCK1-dependent MYPT1 phosphorylation leading to TAK1 activation. Active TAK1 regulates NF-κB and β-catenin signaling, leading to increased cell survival. Thus, inactivation of TAK1 kinase activity promotes apoptosis in CTCL cells