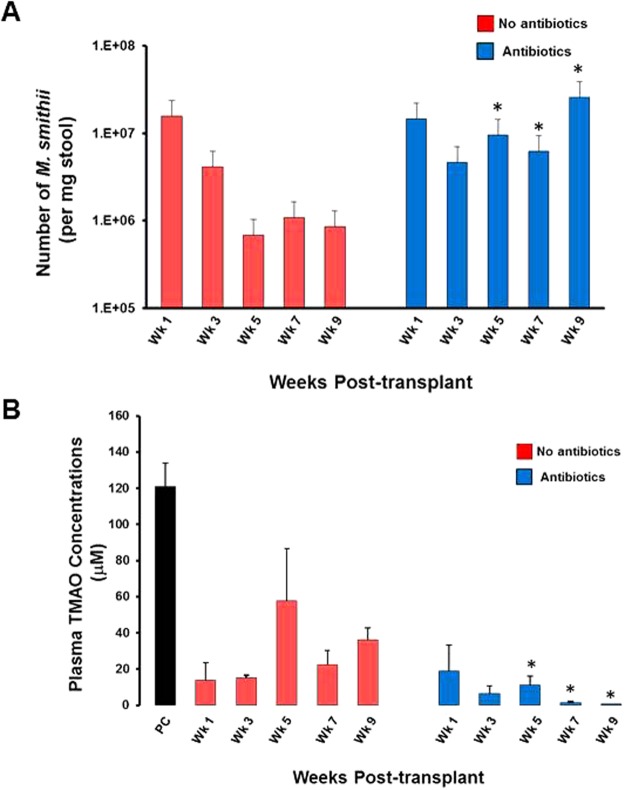
Figure 3.
Repeated transplantation of Apoe−/− mice with M. smithii in presence of antibiotics leads to stable and high level gut colonization and diminishes the plasma TMAO concentrations. (A) To maintain a high level of gut colonization with the MA, M. smithii, transplantation was repeated every 3 weeks for the duration of the study. A second group of mice (+Antibiotics) was also maintained on vancomycin and ampicillin, in addition to receiving repeated transplantations. Weekly blood and stool samples were collected from the mice for 9 weeks. Stool samples were analyzed by q-PCR for MA engraftment levels. (B) Plasma TMAO concentrations in mock- and M. smithii-transplanted Apoe−/− mice (±antibiotics) collected weekly for 9 weeks post-transplantation. Mock-transplanted positive control mice (PC) received high choline/TMA water, similar to M. smithii-transplanted mice, but not antibiotics.