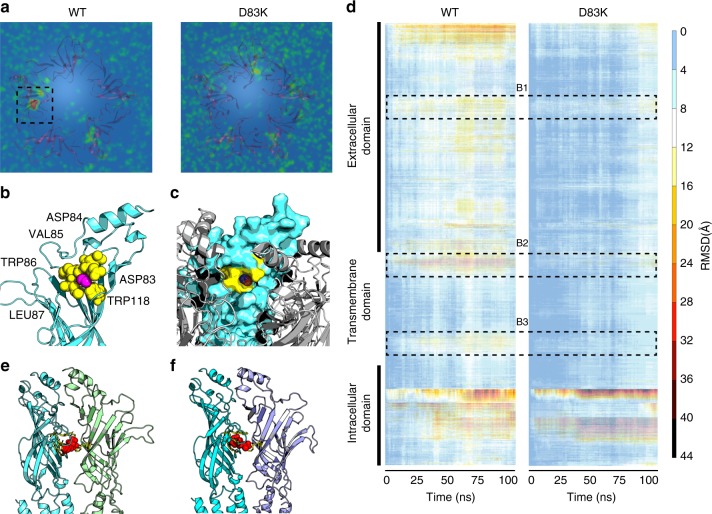
Fig. 1.
Molecular dynamics simulations reveals site of action of ethanol at extracellular domain. MD simulations suggest that ethanol occupies an area in the vicinity of α83 and induces fluctuations in nAChR conformation that are prevented by the D83K mutation of neuromuscular nAChR. a Density distribution (averaged over 100 ns) of ethanol molecules at 25 mM concentration. The selected area (extracellular domain of the α-subunit) shows the space with the highest density (in comparison to other receptor areas such as TMD) of ethanol during the MD simulation. In contrast, the average density distribution of ethanol molecules surrounding the αD83K receptor shows a homogeneous distribution of the molecules within the simulation space, suggesting ethanol is not attracted toward the mutated receptor. b Ethanol molecules interact with a cavity α83–87 (yellow) in the extracellular domain of the α-subunit (light blue). Spherical presentation of the cavity shows αD83, D84, V85, W86, L87 (yellow), and W118 that forms the cavity-base for ethanol molecule (pink). c Accessibility of the cavity by ethanol molecules is shown by surface presentation of the α-subunit. d All-residue RMSD of the backbone structure of WT and D83K receptors further supports the lack of ethanol-induced conformational fluctuations of the D83K receptor in the presence of ethanol. The area B1 relates to amino acids α65–88 that is associated with the accumulation of ethanol particles as in subfigure 1. The area B2 is the interface area between the ECD and TMD comprised by α188–208. B3 is the TMD area associated with the hydrophobic girdle (αL251, S252 and V255, F256). e Acetylcholine molecules (spherical presentation in red) preferably occupy the ligand-binding sites at the α (light blue)-γ(green). f In agreement with experimental studies, the second binding pocket of acetylcholine is located at the α (light blue)-δ (purple) interface area. In particular, the MD simulation shows higher density distribution in a close proximity to the aromatic residues, αTyr 93, αTrp 149, αTyr 190, αTyr 198, and εTrp 55/δTrp 57 that have been reported to relate to acetylcholine binding