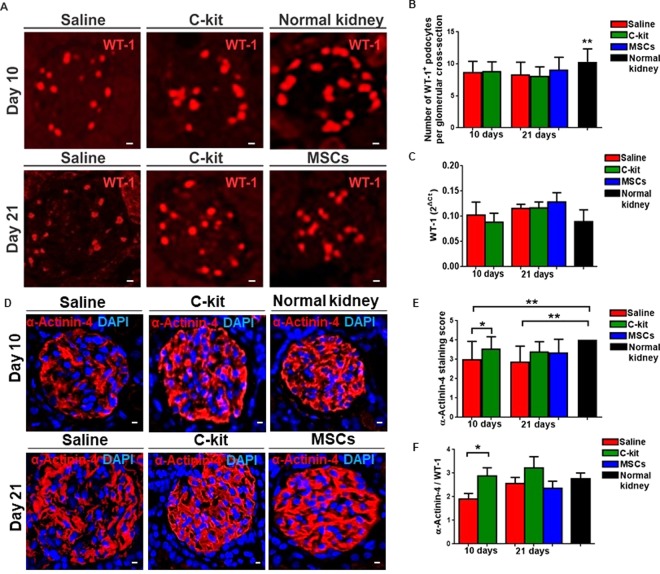
Figure 4.
Kidney-derived c-kit+ progenitor/stem cells promote podocyte recovery by up regulating α-Actinin-4 involved in the podocyte cytoskeleton maintenance, but not by increasing the number of podocytes. (A) Number of podocytes verified by the immunofluorescence staining for WT-1. (B) Normal kidney exhibited higher number of WT-1+ podocytes when compared to all three groups injected with PAN (**P = 0.0017). (C) WT-1 gene expression was not different among groups, by qPCR (2ΔCt). (D) Immunofluorescence staining for α-Actinin-4 and DAPI. (E) Semi-quantitative analyses of α-Actnin-4 immunofluorescence staining score in all groups compared to normal kidney. C-kit treated group at day 10 score was significantly higher than saline group at day 10 (*P = 0.029). Saline group score was lower than normal kidney independently of the time (**P = 0.0084 and **P = 0.003 at days 10 and 21, respectively). (F) Alpha-Actnin-4 gene expression was normalized to WT-1 and was up regulated in the c-kit treated animals when compared to the saline group at day 10 (*P = 0.048), by qPCR (2ΔCt). Error bars represent means ± SEM. Scale bar represents 20 μm for confocal images in (A, D). At day 10, n = 5 and n = 8 for saline and c-kit-treated group, respectively, and n = 12, n = 10, and n = 6 for saline, c-kit, and MSC-treated groups at day 21, respectively.