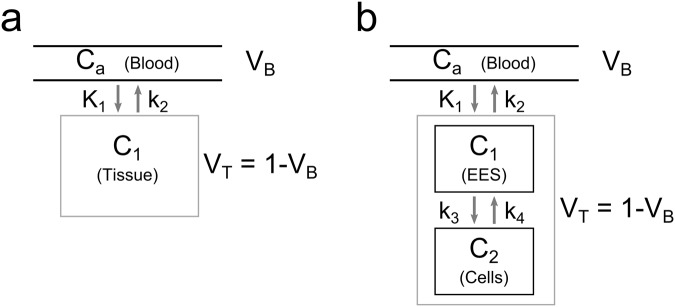
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the used compartment models. Ca is the concentration of tracer in the arterial blood (arterial input function AIF). (a) The one-tissue compartment model (1TCM) describes the exchange of tracer between the arterial blood with the tissue in terms of exchange rates K1(1TCM) and k2(1TCM). In an element of tissue the blood compartment in form of the capillaries occupies the volume fraction VB, whereas the fraction of tissue volume is VT = 1-VB. (b) The more complex two-tissue compartment model (2TCM) separates the tracer concentration in tissue into tracer in the extracellular extravascular space (EES) and in the cells. Tracer is transported from the capillaries into the EES over the blood-brain barrier with rates K1(2TCM), k2(2TCM), and from the EES it is taken up in the cells with rates k3(2TCM), k4(2TCM).