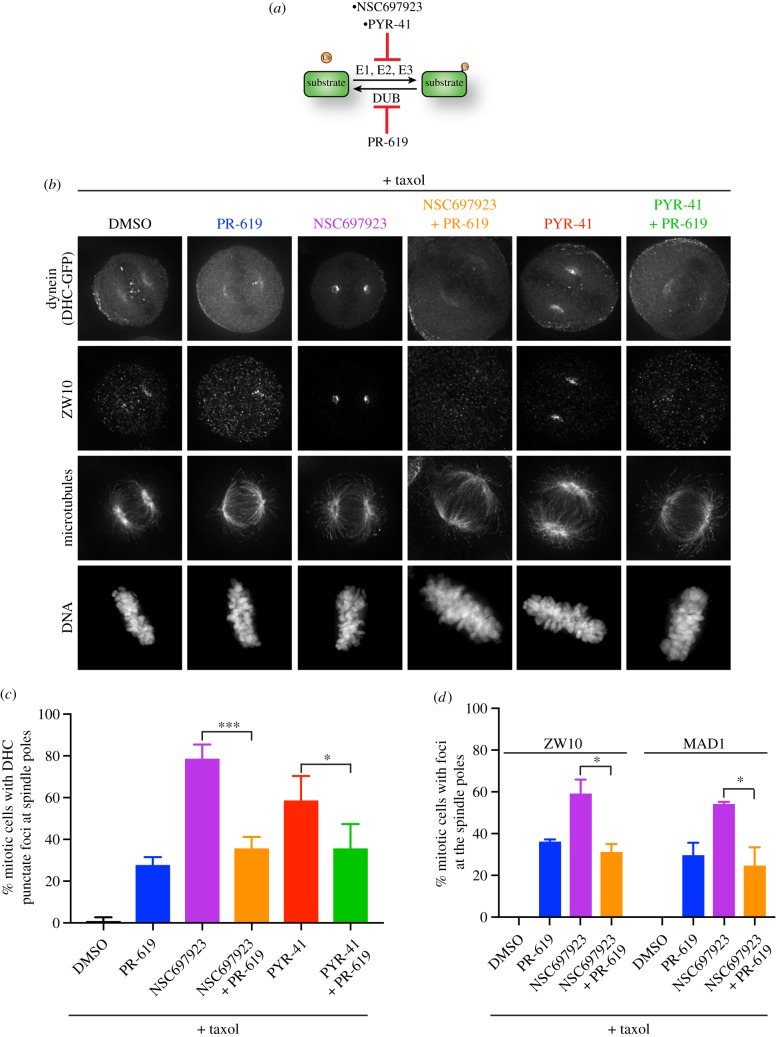
Figure 6.
PR-619 suppresses the relocalization of dynein induced by NSC697923 and PYR-41. (a) Cartoon illustrating the competing actions of the ubiquitinating enzymes with the deubiquitinases. PR-619 is a non-selective deubiquitinase inhibitor. (b) Representative immunofluorescence images of stably expressed dynein heavy chain-GFP (DHC-GFP), ZW10, microtubules (DM1A) and DNA (Hoechst) after treating the cells for 15 min with the indicated compounds. Scale bar, 10 µm. (c) Quantification of the percentage of mitotic cells with punctate foci of dynein heavy chain on the spindle poles for the indicated conditions. The data represent the replicate mean ± s.d. Each replicate included 100 cells. Three to four replicates were analysed for all conditions. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired two-tailed t-tests. ***p ≤ 0.001; *p ≤ 0.05. (d) Quantification of the percentage of mitotic cells with either ZW10 or MAD1 on the spindle poles for the indicated conditions. ZW10 and MAD1 were co-stained in the cells analysed here (and distinct from the cells used to quantify DHC relocalization in panel c above). We note that all cells with spindle pole-localized MAD1 also had ZW10 on the spindle poles. A few cells with weak ZW10 signal did not display detectable MAD1 localization. The data represent the replicate mean ± s.d. Each replicate included 100 cells. Two replicates were analysed for each condition. Statistical significance was determined by unpaired two-tailed t-tests. *p ≤ 0.05.