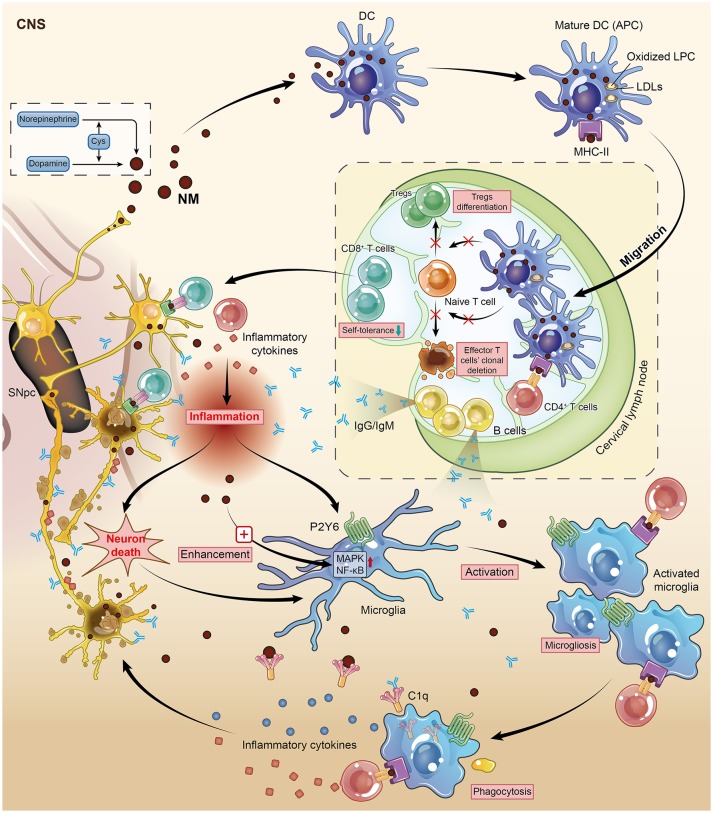
Figure 2.
Neuromelanin (NM) is one of the potential targets during the autoimmune-based pathogenesis of PD. This figure illustrates vividly how DCs and microglia, two kinds of mammalian immune cells, interact with each other and identify NM-rich cells as the object of autoimmune attack on DNs. Mature DCs migrate from the CNS to cervical lymph nodes, resulting in the presentation of NM to naïve T and B cells in a highly immunogenic context. This auto-aggressive loop initiated by DCs along with NM is enhanced and amplified by microglial activation. DC, dendritic cell; DN, dopaminergic neuron; CNS, central nervous system; APC, antigen-presenting cell; Cys, cysteine; Tregs, regulatory T cells.