Figure 2.
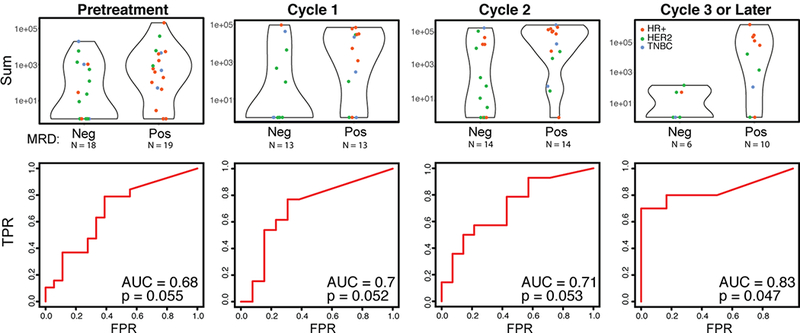
Elevated CTC-Score during presurgical neoadjuvant therapy predicts the probability of residual disease in patients with localized breast cancer at the time of surgical resection. The BL-NEO blood draws were stratified by both treatment cycle (including chemotherapy, endocrine therapy and/or anti-HER2-targeted therapy) and presence of significant residual disease upon surgery, and their CTC scores compared. Breast cancer subtypes are noted (HR+, red; HER2, green; TNBC, blue). High CTC scores in pretreatment and cycles 1 and 2 samples reveal a trend towards presence of significant residual disease, while blood draws from ≥3 cycles of therapy predict significant residual disease. ROC curves, AUC values and p-values for each of the conditions are shown. P-values were computed by comparing the performance of the CTC score to a random predictor.
