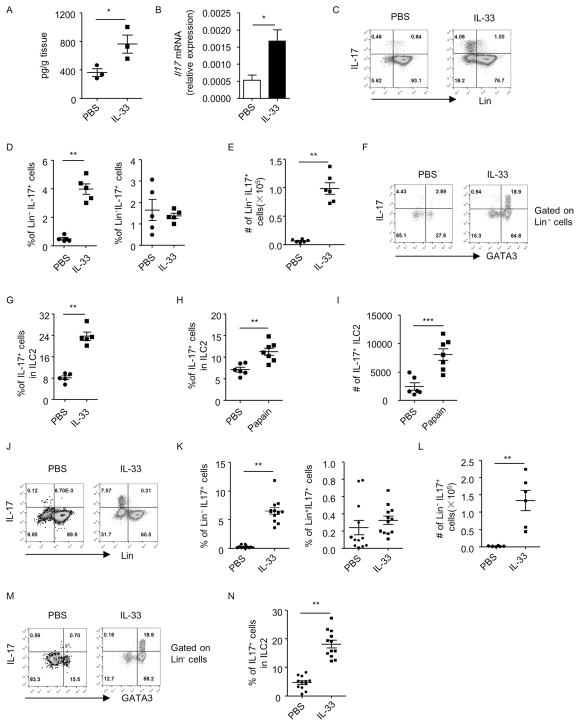
Figure 1. Lung inflammation induces IL-17 production by lung ILC2s independently of the adaptive immune system.
Lung inflammation was induced by IL-33 (A–G and J–N) or papain (H and I) in wild-type (A–I) or Rag1−/− (J–N) mice. Lung lymphocytes were isolated for analysis. (A) Cells were cultured in medium for 48h and supernatants were collected. Level of IL-17 was measured by ELISA and the amount of IL-17 normalized to the weight of the tissue was shown. (B) mRNA expression of IL-17 in lung lymphocytes was analyzed by real-time RT-PCR. (C and J) The expression of lineage markers (Lin) and IL-17 gated on live lymphocytes from indicated groups was analyzed by flow cytometry. (D and K) The percentages of Lin− IL-17+ cells and Lin+IL-17+ cells gated on live lymphocytes were shown. Data are means±SEM. Cell numbers of Lin− IL-17+ cells (E and L) and IL-17+ILC2s (I) from the lung of individual mouse were shown. Data are means±SEM. (F and M) The expression of GATA3 and IL-17 gated on Lin− cells was analyzed by flow cytometry. (G, H and N) Percentages of IL-17+ cells in Lin− GATA3+ (ILC2) were shown. Data are means±SEM.