Figure 4. Volume consumption and blood BCAA concentrations.
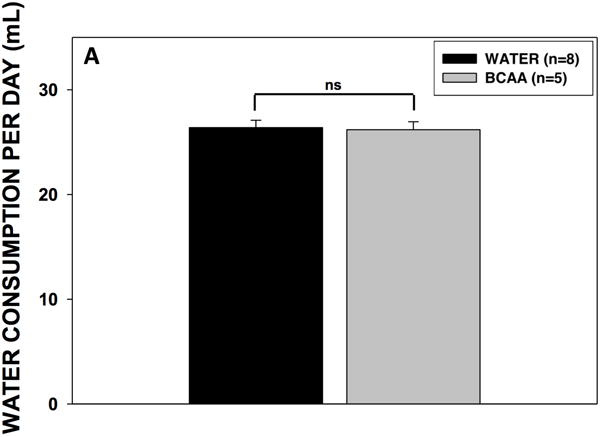
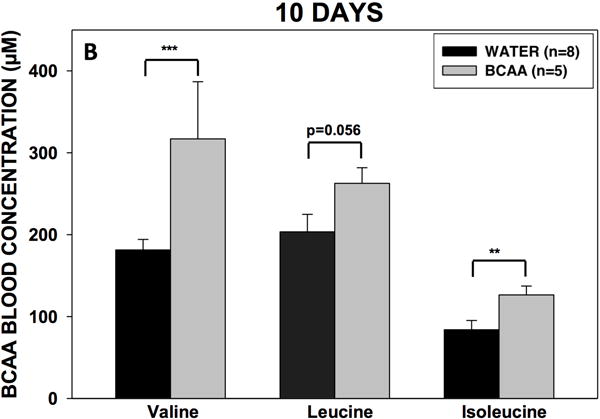
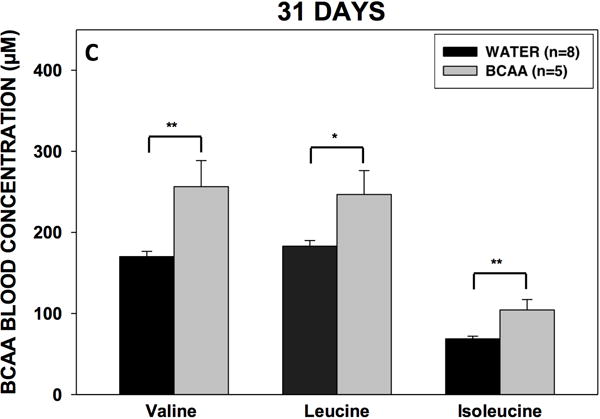
(A) Rats drank either plain water (n=8) or a solution of 4% BCAAs dissolved in water (n=5) ad libitum for 31 days. The water bottles were weighed daily for the duration of the experiment. There were no differences in water consumption between BCAA- and water-treated animals. Data is presented as mean water consumption (mL) per day ± SEM. Blood samples were drawn from the scalp during surgery for placement of methionine sulfoximine pump at 10 days (B) after drinking, and again from the heart during cardiac perfusion at 31 days (C) after drinking. Samples were analyzed for BCAAs using tandem mass spectrometry. At both time points, concentrations of BCAAs were higher in the rats that drank the BCAA solution compared with the rats that drank plain water. Data is presented as mean concentrations of branched-chain amino acids ± SEM. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05.
