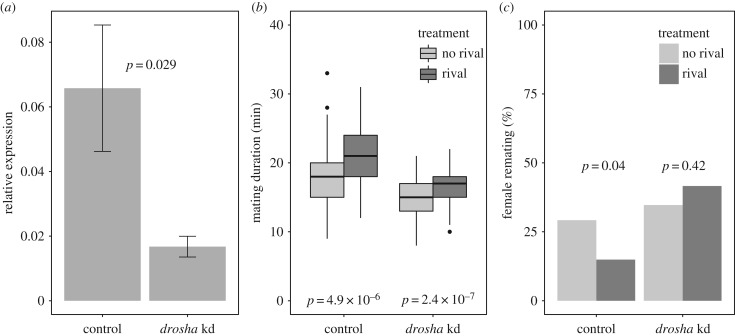
Figure 2.
Manipulations to miRNA biosynthesis abolishes the ability of males to alter ejaculate composition adaptively. (a) Significant knockdown of drosha RNA in male accessory glands (qRT-PCR; relative expression normalized against CG13220 & eIF-1A). The gene for Drosha was individually targeted for knockdown in male accessory glands using main cell promotor-specific GAL4 (Acp26Aa-P-Gal4) to drive the expression of UAS-drosha-IR (inverted repeat), to result in RNA interference of drosha transcripts. Control males generated for each line were from the same genetic background as the knockdowns, but lacked the GAL4 driver. (b) Significant extension to mating duration retained in control and drosha knockdown males following exposure to rivals: control, p = 4.9 × 10−6, n (rivals)=77, n (no rivals) = 96; drosha kd, p = 2.4 × 10−7, n (rivals) = 90, n (no rivals) = 97. (c) Loss of ability of drosha knockdown ejaculates (ns) to reduce female receptivity following exposure to rivals, response retained in controls (control, p = 0.04, n (rivals) = 74, n (no rivals) = 96; drosha kd, p = 0.42, n (rivals) = 89, n (no rivals) = 95).