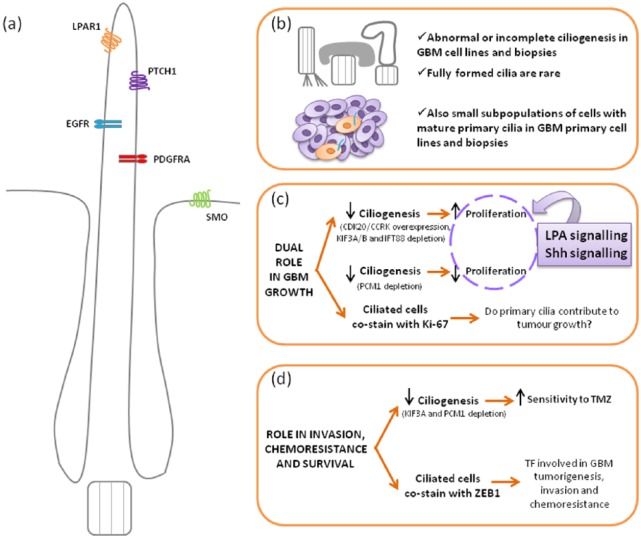
Figure 2.
Schematic view of the main roles of the primary cilium in glioblastoma.
(a) Cartoon illustrating the typical mature primary cilium observed in human astrocytes and GBM samples, with large ciliary pockets; those membrane receptors that have been involved in GBM and localized to cilia are also represented. (b–d) Scheme of the current evidences of ciliary involvement in GBM focusing on three aspects: ciliary structure and distribution (b), role of primary cilia in GBM growth (c) and role in survival, chemoresistance and invasion properties (d).
CDK20/CCRK, cyclin-dependent kinase 20/cell-cycle related kinase; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; GBM, glioblastoma; IFT88, intraflagellar transport 88; KIF3A/B, kinesin family member 3A/B; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPAR1, lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1; PCM1, pericentriolar material 1; PDGFRA, platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha; PTCH1, Patched 1; Shh, Sonic hedgehog; SMO, Smoothened, frizzled class receptor; TF, transcription factor; TMZ, temozolomide; ZEB1, zinc finger E-box binding homeobox.