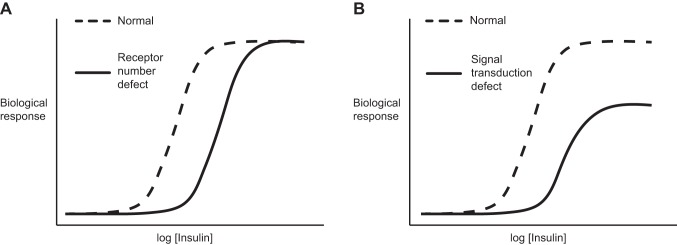
FIGURE 7.
Insulin resistance in dose-response curves. A: in a hypothetical cell with decreased surface insulin receptor (INSR) content, the dose-response curve is right-shifted but the maximal biological response is not decreased unless >90% of surface receptors are lost. B: in a cell with an insulin signal transduction (“post-receptor”) defect, or a combined receptor/post-receptor defect, both a right shift and decreased maximal response are observed. The right graph typifies human obesity-associated insulin resistance in muscle, liver, and adipose tissues.