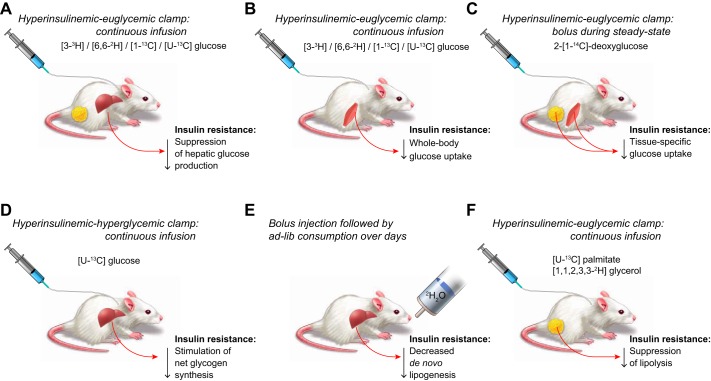
FIGURE 11.
Isotope tracer methods to assess insulin resistance in vivo. Six example methods are illustrated. The experimental protocol and mode of tracer delivery are italicized, the tracer is bolded, and the effect of insulin resistance is at bottom right. A: several glucose isotopomers can be used to trace whole-body glucose turnover, Rd. During a hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp, where Rd and the glucose infusion rate F are both known, endogenous glucose production can be calculated by subtracting F from Rd. Insulin suppression of endogenous glucose production is impaired in insulin-resistant subjects. B: under hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp conditions, 70–80% of Rd is accounted for by skeletal muscle glucose uptake, so skeletal muscle insulin resistance is often accompanied by decreased Rd. C: the nonmetabolizable glucose analogue 2-deoxyglucose (2-DG) is phosphorylated and trapped inside tissues which lack glucose-6-phosphatase (e.g., skeletal muscle and adipose tissue, but not liver). Tissue 2-DG-6-phosphate levels can thus be used to estimate insulin-stimulated glucose uptake, which is decreased in insulin resistance. D: the negligible natural abundance of m+6 glucose makes [U-13C]glucose a useful tracer of hepatic glycogen synthesis, which is decreased in hepatic insulin resistance. To stimulate net hepatic glycogen synthesis, both hyperinsulinemia and hyperglycemia are necessary. E: the incorporation of deuterated or tritiated water into hepatic palmitate yields a measurement of hepatic de novo lipogenesis (DNL) but requires several days of administration to reach isotopic steady state. DNL is decreased in some models of insulin resistance, such as the high-fat-fed rodent. Because insulin regulation of DNL is a slow, transcriptionally mediated process, this method is compatible with the physiology being studied. F: several palmitate and glycerol tracers, including [U-13C]palmitate and [1,1,2,3,3-2H]glycerol, can be used to trace lipolysis. Insulin suppression of lipolysis from white adipose tissue is impaired in adipose insulin resistance. Notably, Ra glycerol under fasting conditions is likely a more accurate measure of lipolysis than Ra palmitate, because palmitate can be re-esterified within the adipocyte.