Figure 1.
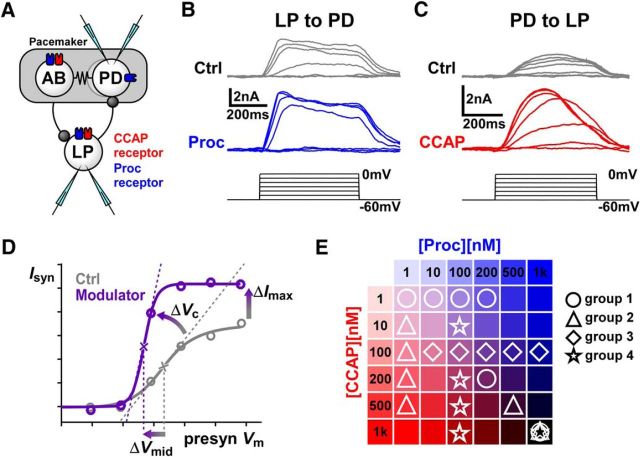
CCAP and Proc modulate the strength and activation curves of the reciprocal synapses between LP and PD neurons. A, Schematic diagram of the synaptic connectivity between the electrically coupled (resistor symbol) pyloric pacemaker neurons AB and PD and the follower LP neuron. Both synapses (stick-and-ball symbols) are inhibitory. Also shown are the known receptor expression for CCAP and putative receptor expression for Proc in these neurons. The experimental protocol involved simultaneous two-electrode voltage-clamp recordings of the PD and LP neurons. B, Example recordings of postsynaptic currents measured in the PD neuron in response to voltage steps in the presynaptic LP neuron in control saline (Ctrl) and in the presence of 1 μm Proc. Measurements were done in 0.1 μm TTX. C, Example recordings of synaptic currents measured in the LP neuron in response to voltage steps in the presynaptic PD neuron in control saline (Ctrl) and in the presence of 1 μm CCAP. Measurements were done in 0.1 μm TTX. D, To measure the modulatory effects, the mean value of the postsynaptic currents was plotted against the presynaptic voltage and fit with a Boltzmann type sigmoidal function. Changes in Imax, Vmid, and Vc were compared in control and in the presence of the modulator. E, Schematic diagram showing how the 18 different combinations of concentrations of the two modulators were divided into four separate groups of experiments.