Figure 3.
AAV2.CR2-Crry Protects Intraretinal Axons
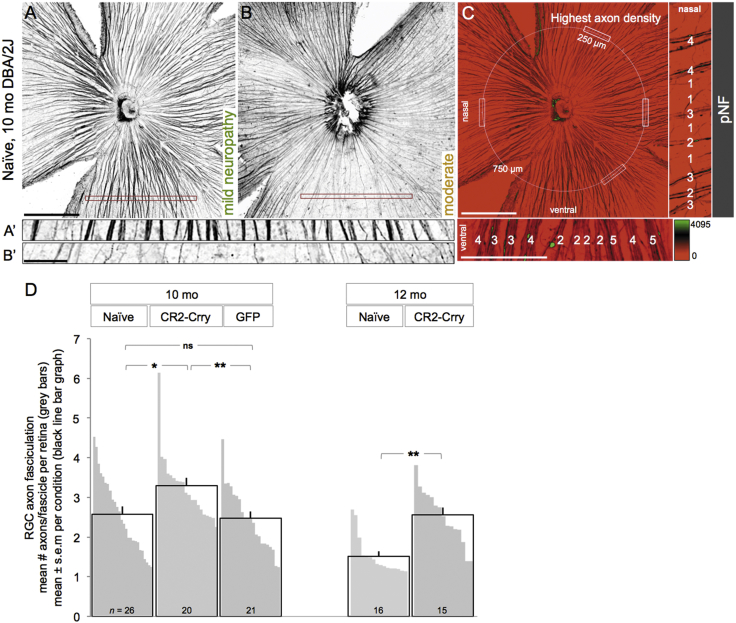
(A–C) Confocal images of pNF-labeled RGC axons on retinal whole mounts, shown as 15-μm maximum-intensity projections through the NFL. Naive, 10-month-old retinas representative of a healthy NFL throughout all quadrants (A) and of an NFL with sectorial degeneration, detectable by fascicle thinning and loss (B). Insets show high-magnification views of retinal sectors with dense fascicles (A’) and a degenerated sector with sparse, single axons, near depletion (B’). The corresponding level of optic neuropathy is indicated for each retina. (C) Sampling method for counting axon numbers per fascicle. Axons bundled together were counted within the healthiest radius of each quadrant, along a 250-μm line, 750 μm from the ONH. Analysis was done at high magnification in pseudocolored images (scaled by fluorescence intensity), as shown in the insets (numbers of axons per fascicle indicated for samples in the nasal and ventral quadrants). Scale bars, 500 μm (A–C) and 100 μm (insets). (D) Number of axons per fascicle expressed as mean per experimental group (black line bars) and as mean per individual retina (gray bars). For example, the retinas shown in (A) and (B) have, respectively, 3.4 and 2 axons/fascicle on average. See Table 7 for statistical analysis.