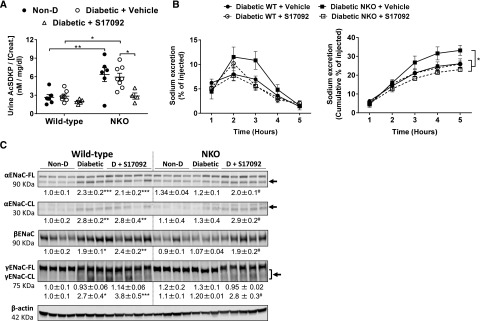
Figure 7.
Inhibition of AcSDKP synthesis eliminates the beneficial effects observed in diabetic NKO mice. (A) AcSDKP was assessed by ELISA in urine samples of WT and NKO diabetic mice receiving either S17092 or vehicle and their respective nondiabetic (Non-D) controls; n=5–8. (B) Mice were challenged with an i.p. bolus of warmed saline equivalent to 10% of their body weight and placed in metabolic cages for hourly urine collection. Plots represent the fraction of injected sodium (left panel) and the accumulated excretion of sodium (right panel) over a 5-hour collection period. *P<0.05; **P<0.01. n=3–5. Data are represented as individual values for each mouse (dots). Horizontal bars represent the mean±SEM. (C) The full-length (FL) and the cleaved (CL) active portions of the ENaC α and γ subunits as well as βENaC were analyzed in kidney homogenates. Immunoblots were performed with a constant amount of protein per lane; β-actin was used as loading control. Relative abundance from each group is displayed below the corresponding blot. Non-D WT group was considered as 1. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 versus WT (Non-D) controls; #P<0.05 versus diabetic NKO+vehicle. n=3–8 per group.