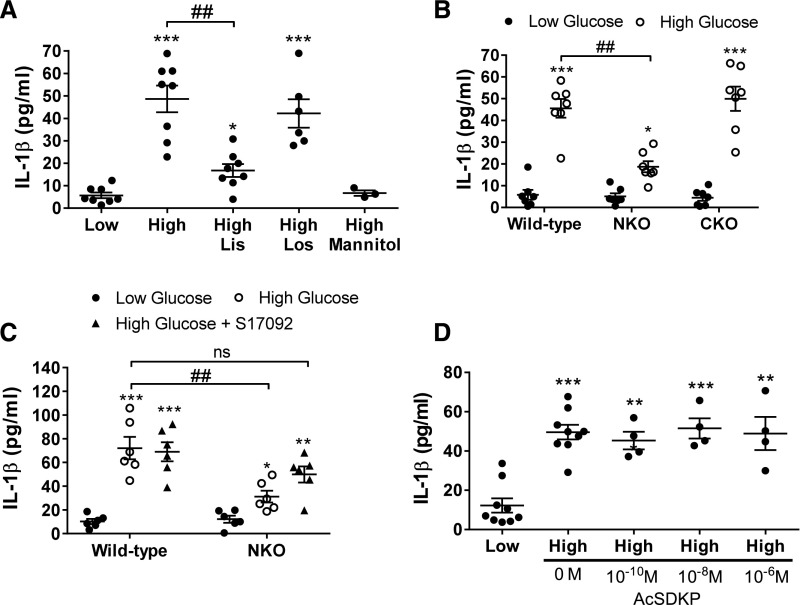
Figure 9.
Lacking a functional ACE N-domain blunts the release of IL-1β from renal tubular epithelial cells in response to high glucose. (A) A primary cell culture of renal tubular epithelial cells from WT mice was established. After 7 days of culture, the glucose concentration of the culture media was increased from 5 (low) to 30 mM (high) for 24 hours, with or without lisinopril (Lis, 10 μM) or losartan (Los, 100 μM). (B) Renal tubular epithelial cells obtained from WT, NKO, and CKO mice were exposed to low and high glucose. (C) Renal tubular epithelial cells from WT and NKO were exposed to low, high, and high glucose plus S17092 (50 µM). (D) Renal tubular epithelial cells from WT mice were exposed to low; high; and high glucose plus 10−10, 10−8, or 10−6 M AcSDKP. IL-1β was evaluated in the culture media by ELISA. *P<0.05; **P<0.01; ***P<0.001 versus WT low glucose; ##P<0.01. Each dot represents an individual experiment. Horizontal bars represent the mean±SEM.