Figure 1. Functional interaction of RNR-α with nuclear protein ZRANB3.
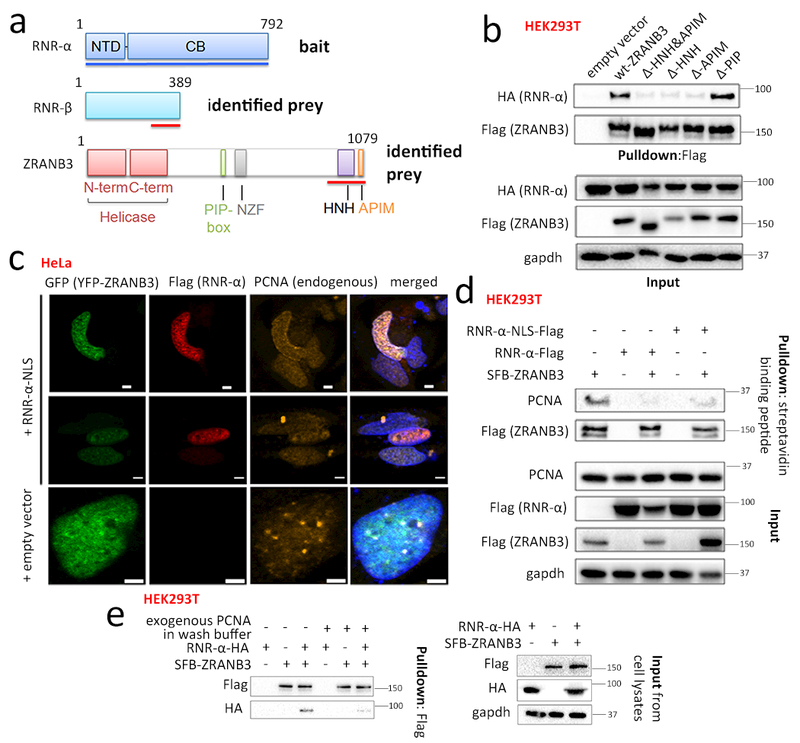
(a) Domains of RNR-α (NTD=N-terminal domain; CB=catalytic body), RNR-β, and ZRANB3 (PIP-box=PCNA-interacting motif; NZF=Npl4 Zinc Finger; HNH=homing endonuclease; APIM=AlkB-homolog-2 PCNA-interacting motif). Red lines show interacting domains in Y2H. See also Supplementary Fig. 1a. (b) Co-IP of Flag-ZRANB3-deletion-mutants with RNR-α in HEK293T. See also Supplementary Fig. 1b–e and 2–3. (c) In transiently transfected HeLa cells: nuclear RNR-α colocalizes with ZRANB3. Scale bars, 2 μm. Although PCNA foci colocalize with ZRANB3 as reported30,31 (Row 3), this association is reduced upon RNR-α-NLS expression (Row 1–2). IF images are representatives of independent cells shown in Supplementary Fig. 4b. See also Supplementary Fig. 4–8. (d) Overexpression of wt-RNR-α (NLS- or no-NLS-tagged) reduces the ZRANB3—PCNA-interaction. HEK293T cells were transfected with indicated plasmids and SFB-tagged-ZRANB3 in lysates was enriched using streptavidin (note: SFB tag contains a streptavidin-binding peptide). See Supplementary Fig. 3b for quantitation. (e) Recombinant His5-PCNA rapidly displaces ZRANB3-bound RNR-α-HA. HEK293T cells ectopically co-expressing RNR-α-HA and SFB-ZRANB3 were lysed and the (SFB-ZRANB3)–(RNR-α-HA) complex was immuno-precipitated using anti-Flag resin (note: SFB tag contains Flag-peptide sequence). The amount of RNR-α-HA co-IP-ed with SFB-ZRANB3 diminished when the washing steps post IP were performed with 5 μM purified, recombinant His5-PCNA. See also Supplementary Fig. 3c–d. For full-view blots and cell cycle data relevant to Fig. 1 and supplementary figures referred to above, see Supplementary Fig. 32 and 35–39. WB images are representatives of n=3 [Fig. 1(b)] or 2 [Fig. 1(c-d)] independent experiments.
