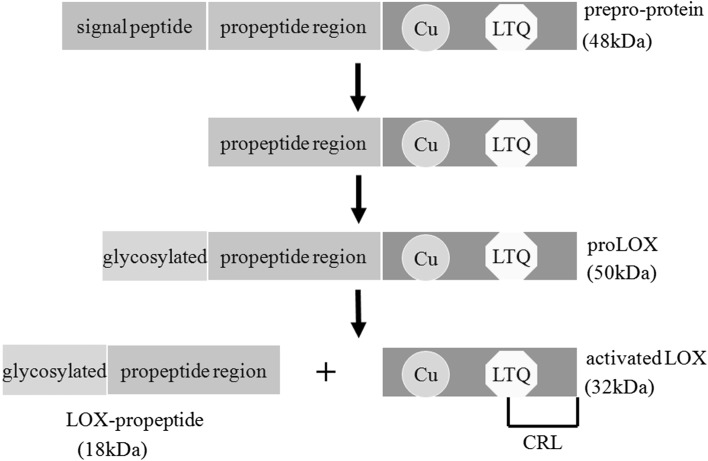
Fig. 1.
The synthesis of activated lysyl oxidases. The output of the process is the removal of the N-terminal signal peptide sequence of human LOX in the endoplasmic reticulum. Then the propeptide domain is N-glycosylated in Golgi and the 50-kDa pro-protein (proLOX) is generated. The proLOX is cleaved by procollagen C-proteinase, mainly bone morphogenic protein-1 (BMP-1), leading to the formation of activated LOX and LOX-propeptide (LOX-PP). In the carboxyl (C)-terminus, the copper binding domain (Cu), the lysyl-tyrosyl quinone (LTQ) residues, and the cytokine receptor-like (CRL) domain are highly conserved in each member of the LOX family