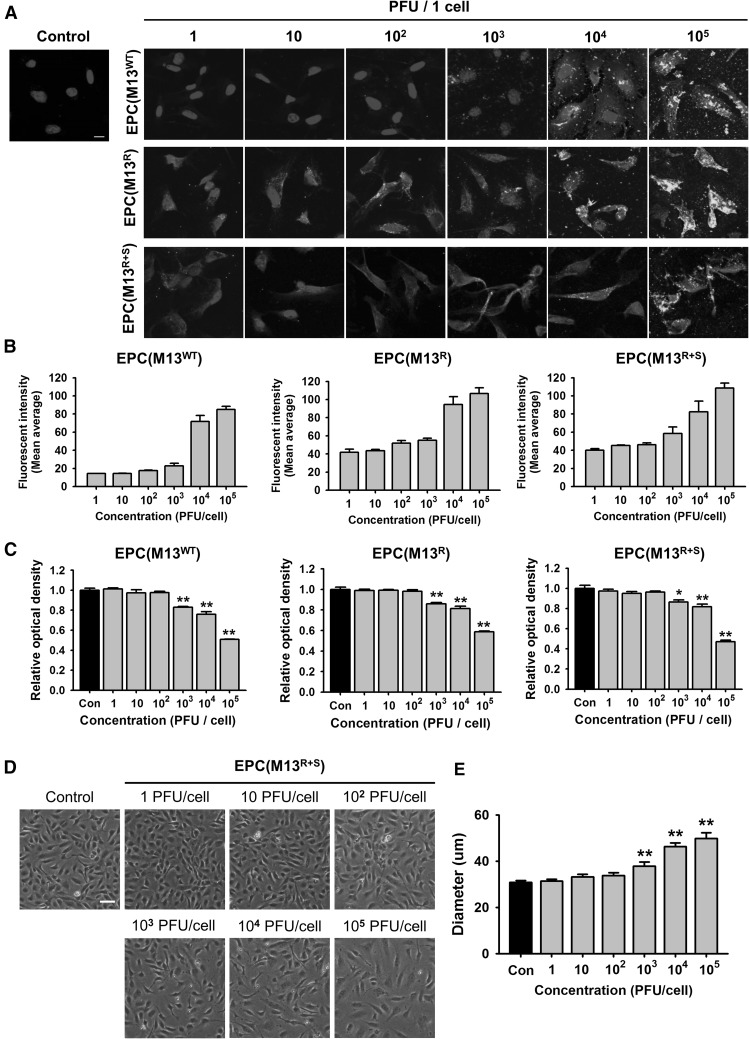
Fig. 2.
Effect of the engineered M13 nanophage on the EPCs. A Adhesion of the wild-type M13 phage (M13WT) and the engineered M13 phages displaying RGD (M13R) or RGD and SDKP (M13R+S) on the EPCs. The M13 phages were immunostained with anti-M13 bacteriophage antibody (green). The nuclei were stained with DAPI (Blue). Scale bar = 10 μm. B Quantification of adhesion of the engineered M13 phage at various concentrations (0–105 plaque forming unit (PFU)/cell) on the EPCs. C After treatment with the engineered M13 phage (0–105 PFU/cell), the viability of the EPCs was assessed. Values are expressed as the mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM). **p < 0.01 versus control. D The morphologies of the EPCs after treatment with the M13 phage displaying RGD and SDKP (0–105 PFU/cell) for 24 h. Scale bar = 50 μm. E Quantification of the diameter of the EPCs after treatment with the M13 phage displaying RGD and SDKP. Values are expressed as the mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01 versus control. (Color figure online)