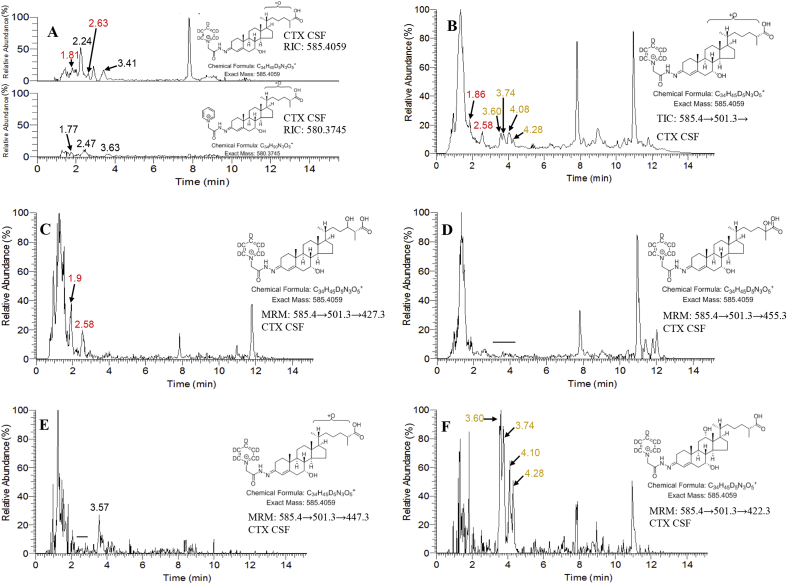
Fig. 6.
Analysis of CSF from a CTX patient. (A) LC-HRMS RICs (585.4059 ± 10 ppm, upper panel; 580.3745 ± 10 ppm, lower panel). The upper panel shows CTX CSF (SPE1-Fr1A) treated with cholesterol oxidase followed by [2H5]GP reagent, while the lower panel shows CTX CSF (SPE1-Fr1B) treated with [2H0]GP reagent in the absence of cholesterol oxidase. The RICs for [2H5]GP derivatised and [2H0]GP derivatised acids are plotted with the same y-axis. Data was acquired in the Orbitrap analyser. (B) LC-MS3 (585.4→501.3→) TIC appropriate to [2H5]GP derivatised dihydroxy-3-oxocholest-4-en-26-oic acids. LC-MS3 MRM transitions appropriate to (C) CA4-7α,24-diol-3-one, (D) CA4-7α,25-diol-3-one, (E) CA4-7α,x-diol-3-one and (F) CA4-7α,12α-diol-3-one. In (D) and (E) the horizontal bars indicate where the targeted acids are expected to elute. The MRMs in (C–F) were generated from data acquired in the LIT analyser of the Orbitrap Elite hybrid instrument with an m/z window of ±0.4. Chromatograms displayed in Fig. 5, Fig. 6 were recorded on different days and show a time shift of about 0.4 min for the later eluting peaks. Retention times were correlated by the analysis of QC samples within in each sample batch. Peaks are colour coded as in Fig. 3.