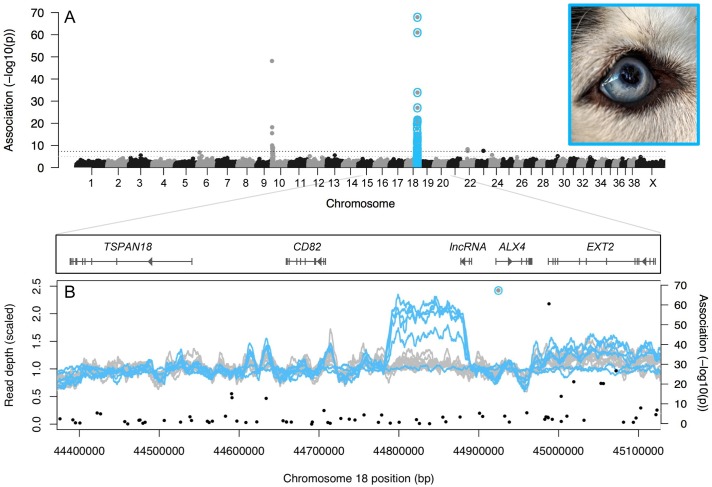
Fig 1.
A) Manhattan plot of associations with blue vs. brown eyes across the genomes of 3,180 dogs. Horizontal lines represent the thresholds for suggestive (grey; P < 1x10-5) and significant (black; P < 5x10-8) associations. B) Read depth (scaled by the average depth across the interval for each dog) in 10-kb sliding windows across the CFA18 GWAS peak region, for the six Siberian Huskies with publicly available whole genome sequence data (blue) and 11 dogs from other breeds (grey). Five of the six huskies and five of the 11 other breeds carry the GWAS allele associated with blue eyes (dot at 44,924,848). Black vertical lines indicate paired-end reads that aligned 98.6-kb from their mate and in an opposite orientation. Photo credit: Aleksey Gnilenkov (Flickr).