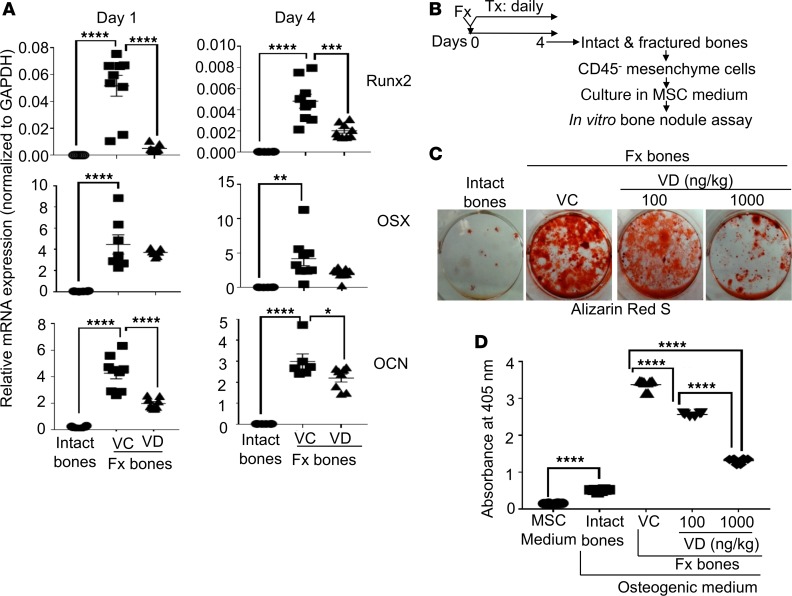
Figure 7. Local s.c. treatment with 1,25(OH)2D during the proinflammatory stage compromised the osteogenic potential of MSCs at fracture sites.
(A) B6 mice were subjected to fracture surgery (Fx). Immediately after the fracture surgery, the animals received a daily s.c. dose of either vehicle control (VC) or 100 ng/kg/mouse 1,25(OH)2D (VD) at fracture sites. At days 1 and 4, intact (intact bones) and fractured (Fx bones) bones were examined for the mRNA expression of runx2, osterix (OSX), and osteocalcin (OCN) by qPCR. (B) B6 mice were subjected to fracture surgery. Immediately after the fracture surgery, the animals received a daily s.c. dose of VC, 100 ng/kg/mouse 1,25(OH)2D (VD), or 1,000 ng/kg/mouse 1,25(OH)2D (VD). At day 4, intact and fractured bones were collected for isolating CD45– mesenchyme cells. The purified cells were cultured in an MSC medium. Upon reaching 70%–80% confluence, an equal number of the cells were used for the in vitro bone nodule assay. (C) Representative images of Alizarin Red S staining at day 21 of the bone nodule assay. (D) Cumulative data of C. Where applicable, data are mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001, ANOVA, n = (3-5).